All businesses need a way to detect vulnerabilities on their networks. This is especially true for larger businesses and those with sensitive data—banking, government, finance, law, health care, and education are all industries in which safeguarding network data and infrastructure is paramount. But smaller businesses must also ensure their information is secure, without pouring all their IT time and resources into the task. This is where automated vulnerability management (VM) tools come in.
So, what are the best vulnerability scanners on the market today? In this article, I review the top vulnerability scanners, both paid and free. Spoiler alert: Network Configuration Manager stands out as my pick for best overall tool, as it offers not only important monitoring insights but also a way to fix configuration issues quickly across mass devices. My top pick for a free vulnerability scanner is Wireshark, a well-known and popular option, for good reason.
However you choose to invest your resources, a fundamental understanding of network vulnerability management is key. This article also outlines the basics of vulnerability management every IT pro needs to know so you get the most benefits out of your scanning tool.
Vulnerability Management Basics
Common Security Vulnerability Causes
Identify Vulnerability Risks
Vulnerability Management Techniques
Types of Vulnerability Scanners
What Do Vulnerability Scanners Do?
Best Paid Tools
Best Free Tools
Vulnerability Monitoring Issues
The Basics of Vulnerability Management
Do you know if your IT infrastructure is protected? Even if end users can currently access their files and your network connectivity seems fine, you can’t assume the security of your network. Every network has some security hole that bad actors or malware could exploit. The goal is to minimize these vulnerabilities as much as possible, which is an ongoing task, considering your network is constantly used and changed while security threats continually evolve.
Vulnerability management has many components. You might think installing antivirus software, for instance, is enough, when in fact, it tends to leave you playing damage control. It’s important to take preventative measures to preclude security issues in the first place. Vulnerability scanning tools can make a difference.
Essentially, vulnerability scanning software can help IT security admins with the following tasks.
- Identifying vulnerabilities – Admins need to be able to identify security holes in their network, across workstations, servers, firewalls, and more. It takes automated software to catch as many of these vulnerabilities as possible. While very small offices that happen to have robust IT resources may be tempted to manage network security manually, businesses of any size will benefit from the time-saving assistance an automated tool provides.
- Evaluating risks – Not all vulnerabilities are equally urgent. Scanning tools can classify and categorize vulnerabilities to help admins prioritize the most worrisome issues.
- Addressing problems – Once you’ve identified priority risks, addressing them can be a daunting task. The right tool can help you automate the process of provisioning devices.
- Reporting on security gaps – Even after vulnerabilities have been addressed, it’s still important for admins to show compliance with relevant regulations. Scanning software can facilitate the creation of reports about a network’s security status.
What Causes Security Vulnerabilities?
There are countless ways bad actors could compromise a network and steal data. That said, there are common security vulnerabilities to watch out for. Not every network scanning tool will address all these concerns, but you should look for software to help you prioritize some or all of the following threats.
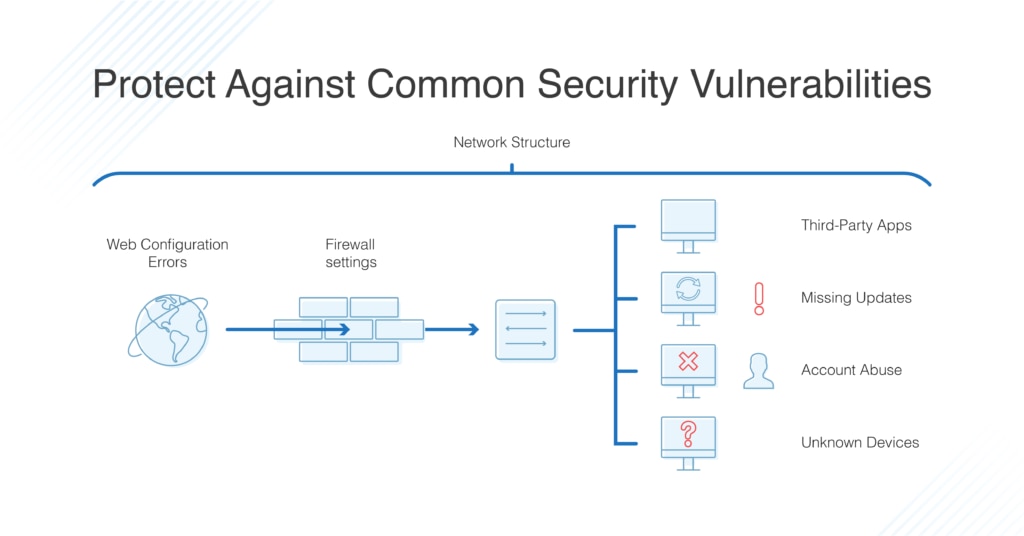
- Network structure – Too many business networks are essentially “open,” which means once an unauthorized user gains access, they have access to all parts of the network. This vulnerability can be prevented with better network segmentation and management of user group privileges.
- Unknown devices – Unidentified or unmanaged assets on your network are never good news. It’s important to make sure only approved devices have access to your ports.
- Account abuse – Unfortunately, insiders sometimes abuse their privileges, causing purposeful or inadvertent leaks of sensitive information, or the misconfiguration of programs, causing additional security holes. Furthermore, admins might allow default credentials, leave unused users or groups in the system, or assign incorrect privileges, all of which pose a security risk.
- Web configuration errors – To ensure website application security, you need to watch out for issues like distributed denial-of-service attacks, HTTP misconfigurations, expired SSL/TLS certificates, and insecure code.
- Security feature configurations – How you manage your security settings and infrastructure could open risks. To avoid vulnerabilities, watch for firewall or OS misconfigurations.
- Third-party applications – There’s a reason no one uses Java anymore. Too many third-party applications open security holes, whether because of how they’re built or how they’re downloaded and implemented. In addition to avoiding these applications, watch out for suspicious downloads, insecure remote desktop sharing software, and software nearing the end of its life.
- Missing updates – One major cause of security issues on networks is basic errors in software and firmware configuration or cases where configuration levels become uneven across the network. Similarly, it’s all too easy to fall behind on updating and patching devices and programs, even if patches are available. Hackers can quickly exploit these gaps.
Evaluating Risks of Vulnerabilities
Vulnerability scanners often produce a long list of risk factors, and admins are rarely able to resolve all identified risks immediately and effectively—it simply requires too many resources to assess and address every single item. Many automated tools provide rankings of risks, from high to low, calculated using factors like how long the risk has been in the system and whether the impact to the system would be major or minor.
However, admins should still be prepared to assess risks on their own if needed and understand the reasoning behind threat assessments so they can take deliberate action in response. Admins should first identify the most critical vulnerabilities and prioritize those items. For each item, consider: if a bad actor exploited this security gap, what would the impact be? Is sensitive data at risk? Does this security hole open a large part of the network to hackers or a limited section?
You also want to consider the likelihood of a bad actor exploiting a security gap: while internal network and physical access are vulnerable to employee actions, external network holes leave your company data open to the world, which is considerably more dangerous. In addition, double-check vulnerabilities to make sure they’re not false positives—there’s no need to spend resources on a nonexistent problem.
The purpose of evaluating security gaps is to prioritize the vulnerabilities requiring urgent attention. Few IT teams have unlimited time and resources for addressing every single item that crosses their paths. In reality, you’ll need to focus on the big-ticket items first, hopefully with automated assistance through your security software.
Top Vulnerability Management Techniques
Vulnerability scanning is a crucial technique for preventing security breaches on your network. Furthermore, it overlaps with other vulnerability management techniques that can provide critical network insights:
- Penetration testing – Also called pen testing, this practice is essentially about hacking your own system before someone else can. You’re ethically examining your own attack surface (or hiring someone else to do so) through attempting to break in and “steal” data. This can be a highly effective way to identify security gaps, although it is time-intensive and potentially costly, making regular manual testing a viable option only for larger, well-resourced companies.
- Breach and attack simulation – This is similar to pen testing but is ongoing, automated, and quantifiable. Essentially, it enables you to ensure your security measures are effective by subjecting them to regular testing and validation. Tools that undertake breach and attack simulation are newer to the market and work differently from vulnerability scanner tools—for one, they’re managed by outside teams, so you must be sure you trust the vendor. Because of the tools’ emphasis on accuracy, they may result in exposures of sensitive data, as well as impacts on performance.
- Antivirus monitoring – Antivirus software is popular, but it takes a limited approach to protect your network. It’s focused on catching and removing malware within the network, while ideally preventing it from entering the network in the first place. These antivirus tools have less to do with managing network security gaps than with addressing specific threats, like ransomware, spyware, Trojans, and the like.
- Web application scanning – Internal networks aren’t the only entities in need of protection. Web application scanning tools look for vulnerabilities within web apps, either by simulating attacks or by analyzing back-end code. They can catch cross-site scripting, SQL injection, path traversal, insecure configurations, and more. These tools work on a similar principle as vulnerability scanners.
- Configuration management – Although many admins are concerned with zero-day attacks, evidence to suggests misconfigurations and missing patches are the major weak points for damaging hacks. Many admins leave these kinds of risks open for months or years without recognizing or remediating them, even if fixes are available. Scanning for and fixing these errors helps ensure consistency across your systems, even when assets change. These measures can also be crucial for compliance.
Types of Vulnerability Scanning and Detection
Admins planning their vulnerability scanning strategy have multiple approaches at their disposal. In fact, you may wish to try out a variety of scan types as part of your overall security management, as testing your system from different angles can help you cover all the bases. As outlined below, two key distinctions concern the location (internal vs. external) and scope (comprehensive vs. limited) of the scan.
- Internal vs. External – With an internal network scan, you’ll want to run threat detection on the local intranet, which will help you understand security holes from the inside. Similarly, admins should test their network as a logged-in user to determine which vulnerabilities would be accessible to trusted users or users who have gained access to the network.
On the other hand, there are benefits to performing an external scan, approaching the evaluation from the wider internet, as many threats arise from intentional and/or automatic outside hacks. Likewise, it’s important to scan the network as an intruder might, to understand what data could fall into the hands of those without trusted network access. - Comprehensive vs. Limited – A comprehensive scan accounts for just about every type of device managed on the network, including servers, desktops, virtual machines, laptops, mobile phones, printers, containers, firewalls, and switches. This means scanning operating systems, installed software, open ports, and user account information. Additionally, the scan might identify unauthorized devices. Ideally, with a comprehensive scan, no risks go overlooked.
However, these scans can use up bandwidth and may be impractical to run often. Limited scans focus on particular devices, like workstations or software, to reveal a more specific security picture.
What Do Vulnerability Scanning and Detection Tools Do?
With so many potential threats popping up on networks and web apps, detecting vulnerabilities is an important task for IT admins. That means using vulnerability scanning tools or similar software programs to detect threats and manage security on managed devices and apps. Whatever type of network vulnerability scanner you choose, look for a tool that accomplishes some or all of the following functions, depending on your needs:
- Weakness detection – The first step of vulnerability scanning is to detect system weaknesses across the network. This could mean using a tool to try to catch and even exploit security gaps as it scans the attack surface. Attempting to hack your own network is a proactive measure to ensure security. Some vulnerability detection tools are more targeted and work to identify missing software patches or firmware updates.
- Vulnerability classification – The second step is to classify vulnerabilities, to prioritize action items for admins. Vulnerabilities could include packet anomalies, missing updates, script errors, and much more, and threats are typically prioritized by a combination of age and calculated risk level. Many tools compare the security issues they discover to updated databases of known vulnerability risks, including the National Vulnerability Database and Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures.
- Countermeasure implementation – Not all security tools both identify issues and give admins a way to automatically address them. Some VM tools are focused on monitoring exclusively, leaving it up to admins to take the next step. But some are built to address device issues, like configuration errors, potentially reaching many devices simultaneously to save admins hours of work. These kinds of automated responses can be incredibly helpful for mitigating risks across large networks.
10 Best Paid Tools for Vulnerability Scanning and Detection
If you’re looking to make a concrete change to your network to help prevent security breaches, I recommend SolarWinds® Network Configuration Manager (NCM). While not what some might classify as a traditional “scanner” tool, NCM does a great job in automatically detecting configuration issues across multi-vendor network devices and can quickly deploy firmware fixes to dozens or hundreds of devices at once.
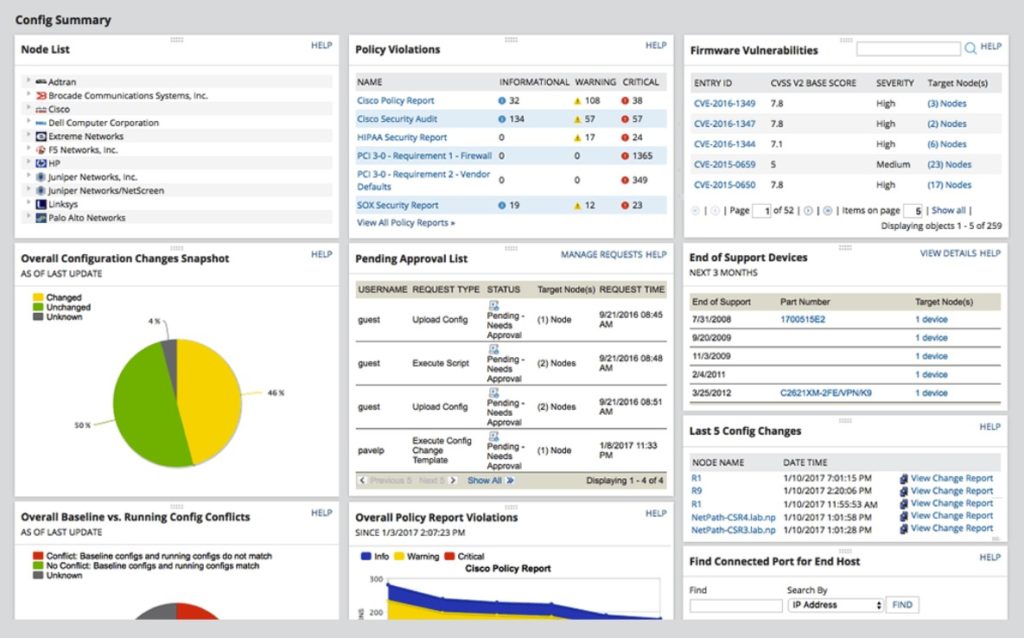
NCM enables you to easily manage device settings known to create vulnerabilities; you can even create your own remediation scripts to keep your devices compliant. Since configuration errors and missing patches are potentially the greatest sources of security breaches, this is an actionable way to prevent attacks, and in my opinion, is a necessary part of any vulnerability management strategy.
NCM offers the most important benefits of vulnerability scanners. For instance, it integrates with the National Vulnerability Database and the Common Vulnerabilities and Exposures database, so you can see what Cisco firmware vulnerabilities are a top security priority. It also helps you save on admin time and resources through automated firewall management and insights into when devices are added or approaching the end of service life. Plus, NCM offers critical robust reporting features for effective vulnerability management. With this tool, you’ll gain a full network inventory, accounting of configuration changes, insight into current compliance status, and other reports to help you plan ahead on security.
You can try it out by downloading a 30-day, full-featured, no-obligation free trial to see how NCM works for you. For such a comprehensive tool, you should find the price more than reasonable. Plus, many SolarWinds products integrate well together, so you can continue to build out your IT capabilities down the line.
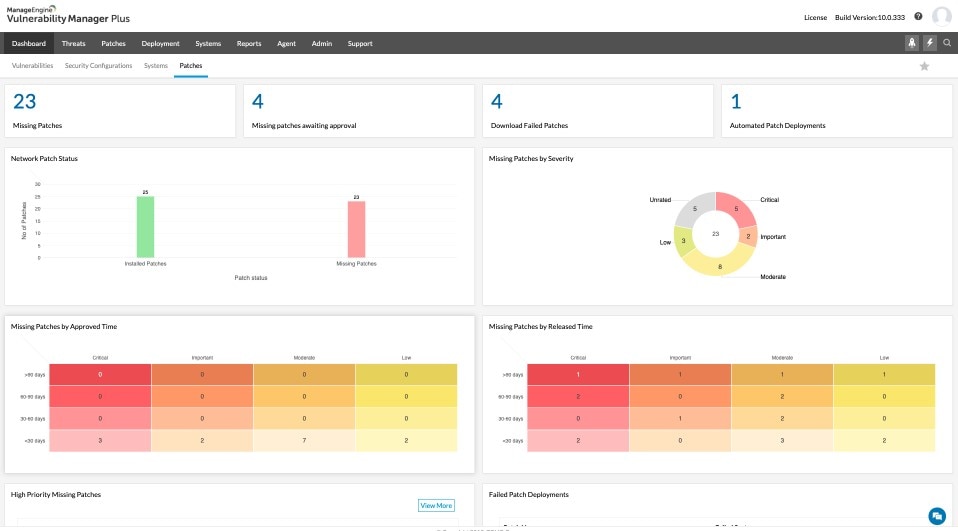
ManageEngine VM software enables some important insights with its vulnerability assessment features. Scan for vulnerabilities in devices, Windows systems, and some third-party applications, and gain an instant ranking of their age and severity. ManageEngine Vulnerability Manager Plus uses an anomaly-based strategy for catching security issues, rather than the database approach.
The tool provides a nice range of capabilities. In addition to helping you manage your antivirus software to make sure it’s up-to-date, it allows you to identify software posing security risks, ports being used for suspicious purposes, and configuration issues.
There are some management tools incorporated into the ManageEngine platform, including configuration deployment and patch management. You can also catch zero-day vulnerabilities and use prebuilt scripts to mitigate them. Despite its many features, this software is generally straightforward to use, although it might be too complicated for smaller environments. It’s free for use on up to 25 computers.
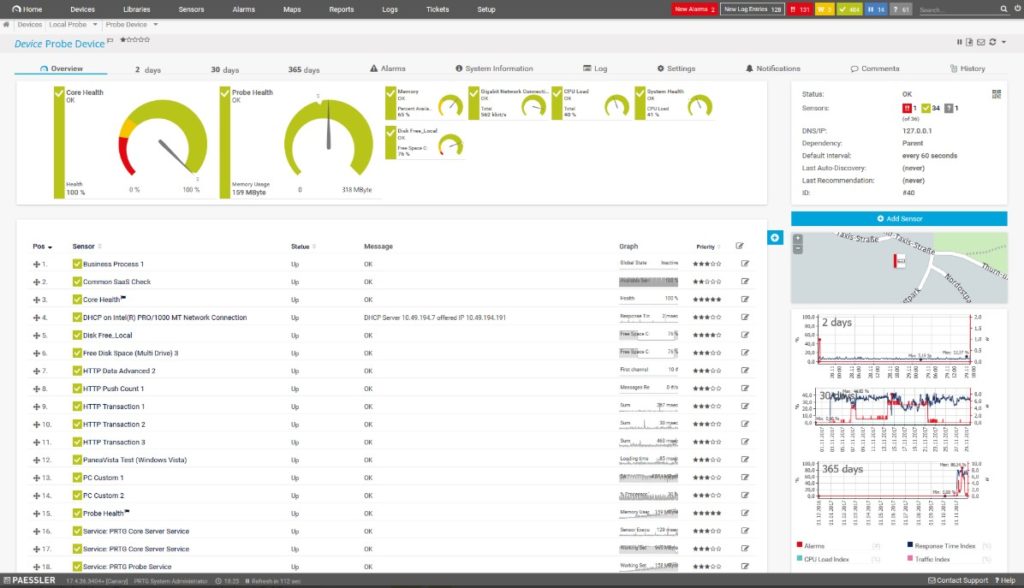
This tool provides thorough infrastructure monitoring, allowing admins to take stock of the network, applications, servers, and more. The platform can track status changes to devices and alert you to any significant changes, as the unusual activity may indicate an intrusion. It can use packet sniffing to scan SNMP trap data and port activity, too.
PRTG is purely a monitoring tool, meaning it doesn’t provide automated assistance with management or resolution. Free for 100 or fewer sensors, it also offers a 30-day free trial with unlimited sensors, allowing you to try out the tool’s full capabilities.
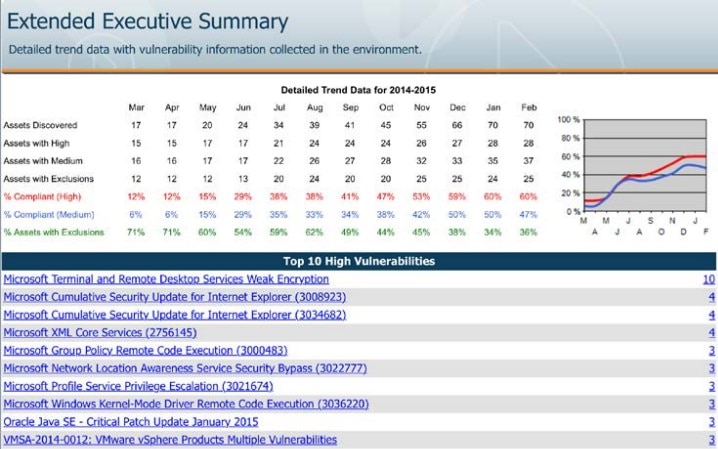
The BeyondTrust Retina tool can scan across your network, web services, containers, databases, virtual environments, and even IoT devices. Its built-in IoT compatibility and audits aren’t found in all scanner tools out there, so this is a great option if you need to manage an array of devices. At the same time, it’s designed to scan without affecting availability or performance. This program compares threats to a vulnerability database rather than relying on anomaly detection.
Retina is focused on monitoring, rather than security management. Thus, while it’s useful and easy to use for understanding your security environment, you would have to integrate the platform with the more expensive Enterprise Vulnerability Management tool for greater coverage.
This is a useful on-premises vulnerability management tool offering a decent starting point for security scanning. Nexpose takes a unique approach to rating risks, using a 1–1000 risk score rather than a High-Medium-Low or 1–10 scale. This detailed rating accounts for the age and exploit kit usage of vulnerabilities. Some users love this; others find it overkill. Nexpose also provides step-by-step instructions for comparing your systems to common policy standards, helping ensure compliance. Though it doesn’t necessarily offer all the features you’ll need for management strategy, it does have an open API, which allows you to integrate its data with other tools.
Tripwire IP360 is an enterprise-grade internet network vulnerability scan software to not only scan all devices and programs across networks, including on-premises, cloud, and container environments, but also locate previously undetected agents. This tool helps automate how admins address vulnerabilities, ranking risks by impact, age, and ease of exploit. And, like Nexpose, it has an open API, allowing you to integrate these vulnerability management features with other management solutions. Otherwise, IP360 is a standard vulnerability scanner.
ImmuniWeb is an AI-based platform offering several vulnerability scanning tools, such as ImmuniWeb Continuous to perform penetration testing to catch security threats and ImmuniWeb Discovery to detect and provide hackability scores based on your assets. It uses machine learning capabilities to quickly detect risks, and supposedly returns zero false positives. There’s a human intelligence element to the tool as well—human pen testers are at work behind the scenes to ensure accuracy. Though too pricey and specific for most organizations, ImmuniWeb may be an option for some DevOps teams.
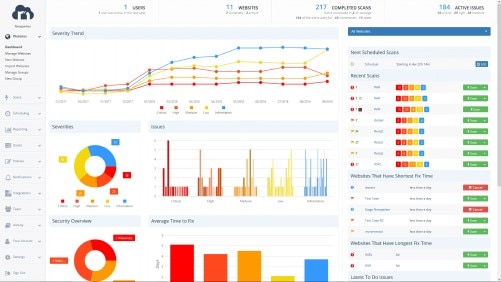
If you’re looking specifically for web application security, this could be a good choice. Netsparker offers a proprietary Proof-Based-Scanning technology, which works to eliminate false positives—a major benefit as you scale your scope. In addition, Netsparker is built to integrate with other management systems, to help automate the vulnerability workflow. This internet vulnerability assessment tool is all about automation and accuracy; you may want to check out the demo to see if that holds true. It’s used by some major clients, including the U.S. Department of Homeland Security.
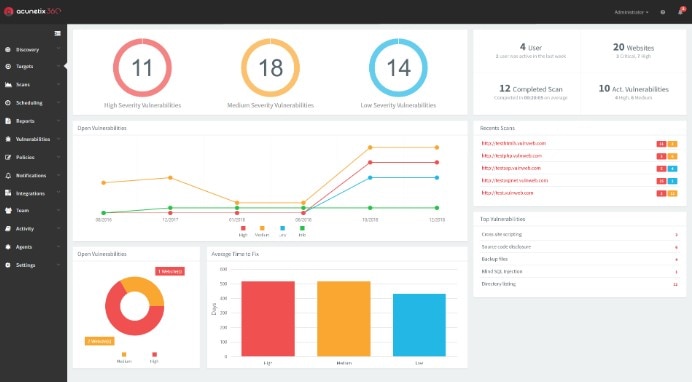
This is another website security scanner, rather than a network scanner. Acunetix touts its ability to detect over 4,500 vulnerabilities in custom, commercial, and open-source applications, with a low false-positive rate. In addition to line-of-code visibility and detailed reports to help you more easily remediate security issues, it gives you the ability to configure your workflow as needed within an appealing visual platform. For teams that manage websites, this kind of flexible tool can be a lifesaver.
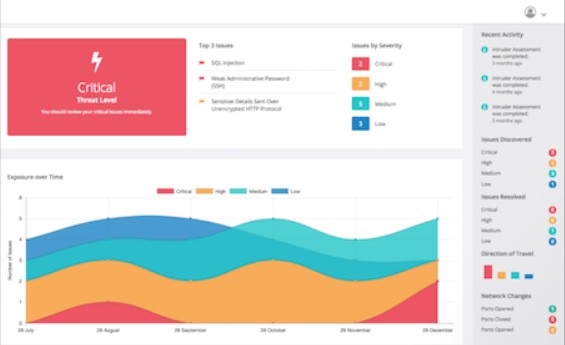
This cloud-based vulnerability scanner takes a streamlined approach to risk detection. Intruder checks configurations, detects bugs in web applications, catches missing patches, and attempts to reduce the false-positive rate. You can connect to your cloud provider to include external IPs and DNS hostnames in your scans. Some teams will appreciate the ability to get notifications on Slack, Jira, and email. Others will find the tool a bit too simplistic for in-depth use, but the price makes it approachable.
5 Best Free Vulnerability Scanners
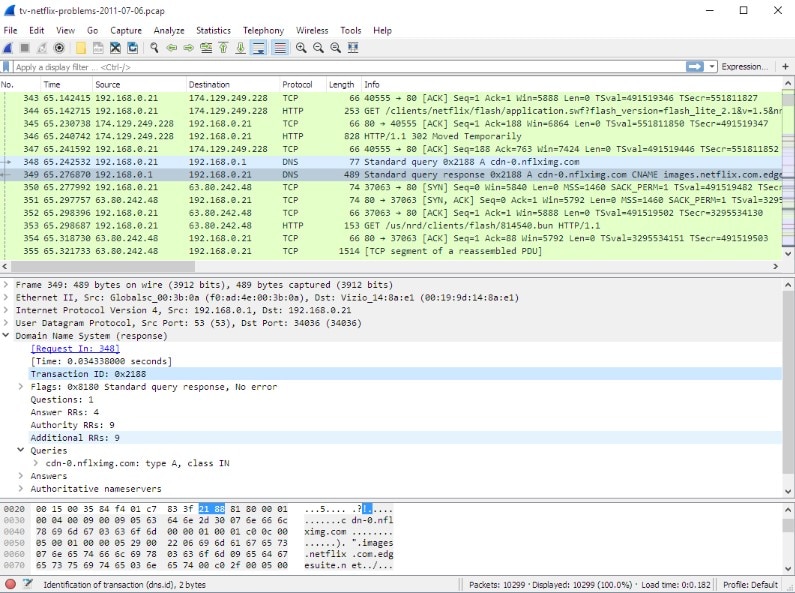
This well-known open-source network protocol analyzer helps with certain vulnerability scanning tasks. The Wireshark free vulnerability scanner relies on packet sniffing to understand network traffic, which helps admins design effective countermeasures. If it detects worrisome traffic, it can help to determine whether it’s an attack or error, categorize the attack, and even implement rules to protect the network. With these capabilities, Wireshark is absolutely a powerful tool. However, like much open-source software, it isn’t necessarily easy to use—be prepared to carefully configure and manage this platform to meet your needs.
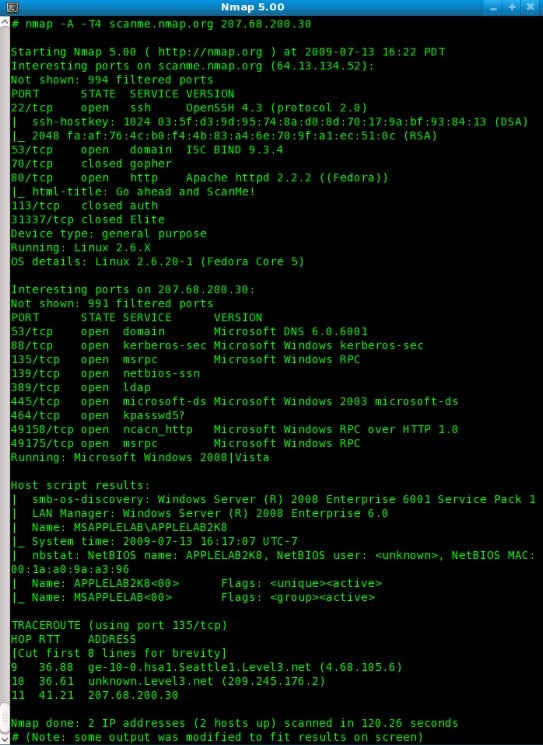
Nmap is a classic open-source tool used by many network admins for basic manual vulnerability management. This free vulnerability scanner basically sends packets and reads responses to discover hosts and services across the network. This could mean host discovery with TCP/ICMP requests, port scanning, version detection, and OS detection. For admins who are comfortable creating scripts, the tool allows for some advanced vulnerability detection as well. Nmap is all about expert-level command-line use and doesn’t offer an intuitive display for easily running scans or interpreting results. Though this makes it the right fit for some professionals, most admins will want a more streamlined approach to vulnerability scanning.

The Open Vulnerability Assessment System (OpenVAS) is a software framework of several services for vulnerability management. It’s a free, open-source tool maintained by Greenbone Networks since 2009. Built to be an all-in-one scanner, it runs from a security feed of over 50,000 vulnerability tests, updated daily. Designed specifically to run in a Linux environment, this free vulnerability scanner is a good option for experienced users who want to perform target scans or pen-testing. Installing and using it has a significant learning curve, and it’s not the right tool for most network admins for that reason. Greenbone also offers a paid product with more regular updates, service guarantees, and customer support.
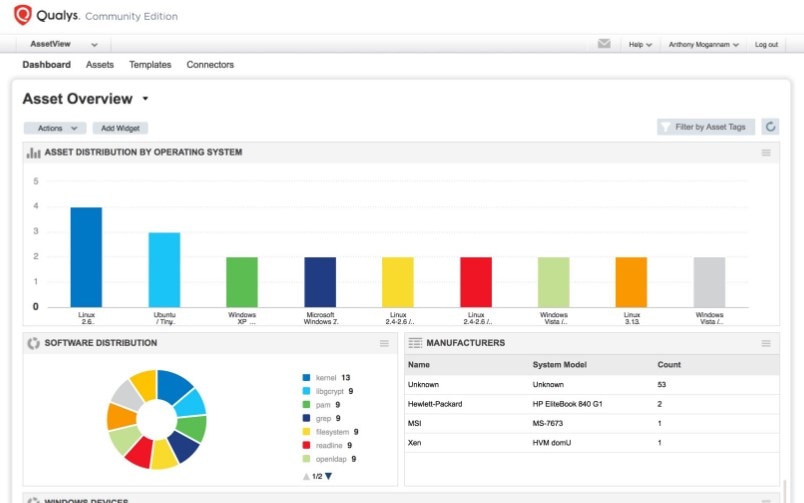
This free, cloud-based service replaces the older Qualys FreeScan tool. Community Edition provides a pared-down version of the Qualys Cloud Platform appropriate for small organizations, as it provides unlimited scanning for 16 internal assets, three external assets, and one URL. It comes with many of the features of the full tool, as the platform draws on information from over three billion yearly vulnerability scans. One advantage of Qualys Community Edition is the ability to search through scan results and create flexible reports. Plus, the interface is appealing to use.
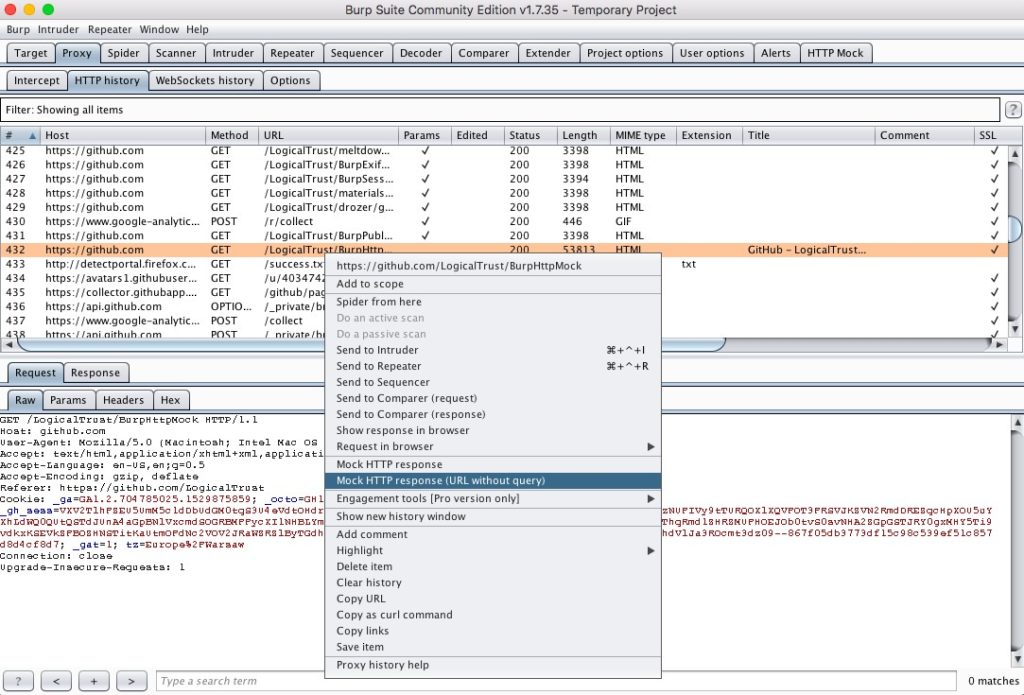
This free version of an internet vulnerability assessment tool is also available at Enterprise and Professional levels. For administrators who want more manual control over their web-based vulnerability scanning, Burp Suite Community Edition is a strong contender. You can manage (intercept and edit) requests and responses, annotate items, and even use match and replace rules to apply custom modifications. You also gain granular control over rules, along with the ability to achieve insight into the site map, view some statistical analysis charts, and access free extensions from the user community. Basically, if you’re interested in building the tool you need for web scanning, Burp is a powerful and free option.
Issues With Vulnerability Monitoring
Vulnerability scanning tools are helpful, but it’s important to know running these programs has the potential to cause issues on your network. For instance, scanners intrude on the running code of target devices, which can lead to errors or reboots. On some networks, scanners take up bandwidth and can cause general performance issues. For this reason, admins may prefer to run scans during off-hours to minimize employee impact. In fact, some scanners are built to minimize this impact. For example, some programs incorporate endpoint agents to push information to the platform, rather than allowing the platform to pull information during the scheduled scan.
Another option is to use adaptive scanning, which detects changes to the network, like an added device and scans that new system immediately. This allows for piecemeal scanning rather than a slower, complete scan.
While there are many types of security software tools on the market, using vulnerability scanning software is a critical first step toward protecting your network while relieving some of the manual VM burdens. Check out a tool like Network Configuration Manager as an all-in-one solution to save time and better manage your vulnerability detection strategy.
