Windows Server Update Services (WSUS), a component of the Windows Server operating system, is a free tool that scans your operating system and Windows software and determines whether anything needs to be updated or patched. Though useful, it’s limited in its functionality—not least because it applies only to products from Microsoft. When you’re trying to roll out patches and updates to numerous pieces of software on every computer on your network, going through multiple programs can be frustrating. You don’t want to only update your Windows software; you want to update all the software in your network.
Fortunately, Windows Server Update Services can be easily complemented with alternative patch management tools, such as software to consolidate all your patching processes into one centralized dashboard. As IT environments grow in complexity, administrators increasingly turn to these WSUS alternatives for better control over their update and patch management. To help you find the right solution for your business, I’ve compiled my picks for WSUS alternative patch management software, including the best Windows update tools.

Jump ahead to the WSUS alternative patching tool review:
What Is WSUS?
Windows Server is a server operating system created by Microsoft for use with enterprise-level systems and networks. It’s intended to provide extensive functionality when it comes to network administration, data storage, security, and distributed applications.
Bundled within Windows Server, Windows Server Update Services is a software update facility that automatically looks at your operating system and Microsoft software and determines which applications or tools need updating or hotfixes. It then performs this task for all the Windows machines on your network.
WSUS is useful in two primary areas: the centralized management of updates and the automation of the update management process. It detects updates to software and downloads them from Microsoft’s servers into a central repository, and gives administrators the ability to either approve any updates or block them if desired. Administrators have the option to prioritize certain updates and manually approve others. Apart from checking for and installing patches and updates, WSUS creates reports on available updates by device, providing a comprehensive inventory of the Microsoft software in your network.
The Importance of Patch Updates
Update and patch management is crucial to network function for a variety of reasons, the main three being security, performance, and compliance.
Security Patches
Having out-of-date or buggy software is a huge security risk. Malware is made to exploit security holes, and if one device gets infected, the user could easily pass this on to others. In other words, if your enterprise ends up with malware, you could pass it to other service providers, users, and clients. This is not only a big problem in terms of the operation of your enterprise but could also have major negative effects on your reputation. Patching and updating work to close off those security holes, so they cannot be targeted by malware.
When a bug arises, it takes time for a patch to be developed, tested, and then disseminated to all users of the software. The users then have to actually apply the patch. In some cases, attackers will try to attack a system on the same day a vulnerability is discovered, before a patch can be developed and applied. This is called a zero-day exploit. Attackers and software companies are competing to see who can either exploit or fix the vulnerability the fastest.
The period between the discovery of a vulnerability and the point at which the number of vulnerable devices (i.e., those not yet updated) becomes insignificant is called the window of vulnerability. Software and OS manufacturers attempt to keep this window as small as possible.
Performance Patches
Software updates and patches are not only important for security reasons, but they also improve the performance of your software. They often include newer or better features, or additional functionality with other tools or add-ons they didn’t have before. In many cases, updates are issued to improve the user experience, and if you haven’t updated your software, you could be missing out on great features. Furthermore, updates and patches issued to address bugs can massively improve organizational efficiency.
Compliance Patches
If you deal with sensitive or private data, you need to ensure you’re meeting your compliance obligations. For example, you may need to show health or financial data is kept secure, and as part of this security, it’s important to demonstrate your software is always kept updated. Many of my picks for WSUS alternatives have the capacity to produce patch reports or WSUS reports to help you demonstrate compliance to auditors.
Key Considerations for Patch Deployment
Certain key factors determine the success of the patches you apply. The two main considerations are the timing of deploying patches and the quality of the patch itself.
Patch Deployment
The timing of your patches is crucial. Security vulnerabilities can be quickly exploited, and in many cases it’s important to install a patch or hotfix as soon as possible. However, if you have a large network with a lot of traffic, applying patches immediately may not be advisable. The bandwidth used by patching will compete against normal network traffic, and the throughput for your normal traffic will decrease.
Patch Quality
The quality of the patch is also important. If a patch hasn’t been tested, like any additional code, it could contain its own security vulnerabilities or bugs. The patch could also introduce changes to APIs and internal interfaces, causing software dependent on these interfaces to unexpectedly break or stop performing efficiently.
Limitations of WSUS
WSUS scans your operating system and Windows software, determines whether anything needs to be patched or updated, and implements the necessary fixes. This free patch tool can be added on to Windows Server, and it enables IT administrators to apply patches across networks rather than handle each device one by one. WSUS provides features in addition to updates and patches, such as bandwidth management, network optimization, reporting capabilities, and multiple language support. Generally, it’s useful for small to medium-size businesses.
As well as WSUS works in this context, the gaps in its functionality can be filled with other third-party or Windows server patching tools. One WSUS alternative is called System Center Configuration Management, or SCCM, a patching tool that works alongside WSUS to keep your Windows system functioning securely and in a healthy way.
WSUS vs. SCCM is a matter of smaller capabilities vs. enterprise-level updating systems. SCCM is generally used for enterprise-level networks and can work with a wider range of operating systems, including Windows NT, Windows IoT, Mac OS X, Linux or UNIX, and several mobile operating systems. SCCM provides services including patch management, software distribution and system deployment, and remote control of devices and network access protection tools.
However, neither of these tools is a one-stop shop. And if you want to update your third-party applications at the same time as you handle your operating system and Windows applications, you’ll benefit from implementing a patch management and update management tool.
Best WSUS Patch Management Tools
In this section, we’ll look at the best Windows update tools that link in with WSUS and SCCM, enabling you to patch and update software through one centralized solution. In addition to saving you time and energy, a good Microsoft WSUS replacement will provide a clear overview of your network and devices on it.
Free WSUS alternatives are few and far between. In most cases, an enterprise in the market for a WSUS alternative will need to pay for a premium solution. For this reason, all the tools on this list will eventually require an investment. If a free trial is available for your preferred tool, I highly recommend you try before you buy.
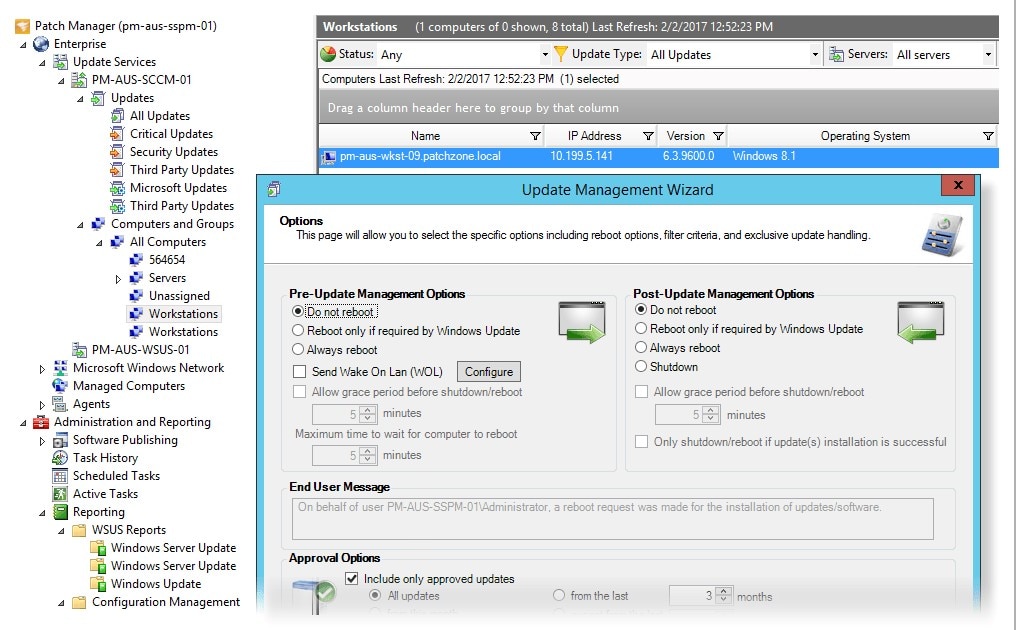
SolarWinds® Patch Manager is my favorite WSUS patch management tool. It offers a highly automated feature set, reporting capabilities, centralized dashboard views, and high-powered patch management abilities in an easy-to-use package.
Patching for Windows desktops and servers can take hours, if not days. With Patch Manager, you can reduce this time to a matter of minutes by using pre-built and tested patches for applications from major vendors including Adobe, Apple, Google, Mozilla, Oracle, and more.
Patch Manager gives you a huge amount of control over where and when patches are applied. You can either set it up to automatically begin patching when an issue is discovered, which increases the security of your network, or to apply patches during network downtime or overnight for reduced network disruption. The tool’s scheduling features include the ability to customize patching schedules based on selections of your choosing—for example, you can set separate patching schedules for different business units or target nodes.
Patch Manager integrates with both WSUS and SCCM, and extends their functionality to allow dynamic patch management, updates, scheduled reboots and patches, WSUS reporting, and other services in a centralized dashboard. You can apply Windows patches and system updates alongside patches and updates to third-party software, which saves time and gives you a broad overview of the patch status across network devices. This centralized patching system also helps determine whether WSUS updates have been applied correctly and in working to fix any issues. Furthermore, a feature called PackageBoot allows you to create pre- and post-deployment scenarios to make sure your patches will deploy successfully.
For compliance, Patch Manager offers a wide range of reports, including WSUS reports, making it easy to show auditors and stakeholders you’re meeting requirements.
Patch Manager is without a doubt an excellent centralized solution for enterprise IT management and network administration. It includes every tool you need to link in with WSUS and SCCM and can also work with third-party applications to ensure your entire system is kept secure.
You can download a free trial of SolarWinds Patch Manager for up to 30 days. You can also look at SolarWinds free WSUS alternative, a WSUS client diagnostic tool to validate WSUS configurations, test WSUS connections and determine sources of failure, and suggest ways to repair WSUS errors. Although this WSUS alternative is limited to diagnosis and doesn’t include the premium features of Patch Manager, it’s a lightweight download useful for basic patch management.
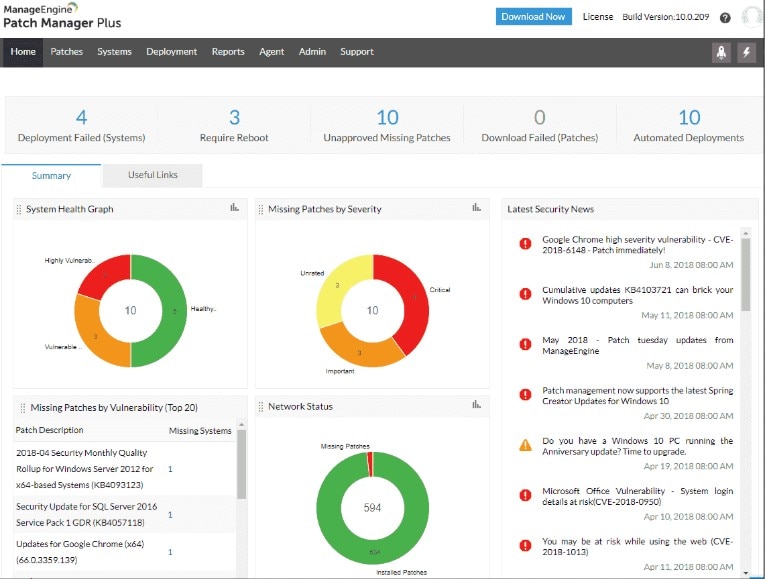
Patch Connect Plus by ManageEngine is a high-quality alternative Windows update tool and works with SCCM as well as third-party applications. It fully integrates with SCCM and provides automatic third-party patching.
Once a patch has been published to the WSUS library, Patch Connect Plus will check to make sure WSUS and SCCM are synced, and the SCCM console can access the patches. It can then automatically deploy these patches onto the relevant systems. Once a patch is deployed, Patch Connect Plus will report on the sync status, publishing status, newly supported applications, expiration of the patch certificate, and any deployment task failures.
The tool has been developed to not only allow you to update third-party applications, but also to install and manage them through the SCCM console. The Applications Management feature provides a repository of available third-party applications, with predefined application templates and both pre- and post-deployment scripts. Templates include actions such as restricting the application from having a start menu icon, taskbar icon, or desktop shortcut, as well as options to uninstall older patches.
You can view any available third-party updates in their own tab, so you won’t be overwhelmed with information. But if you want to browse through this list, it’s easy to find.
One of the most time-consuming parts of patching all the applications and devices on your network is going through and selecting each one and getting the process started. Patch Connect Plus includes an auto-detect feature to look at which applications have been newly added to your network, then automatically publish the patches for those applications.
Finally, you can view comprehensive reports on which computers are missing recent updates, or which have had incomplete or failed patches. These detailed reports provide a full overview of third-party patch deployment, so you can keep an eye on any vulnerable areas of your system in need of additional attention.
ManageEngine Patch Connect Plus offers a free trial for 30 days. You can also try out a demo either in the cloud or on-premises.
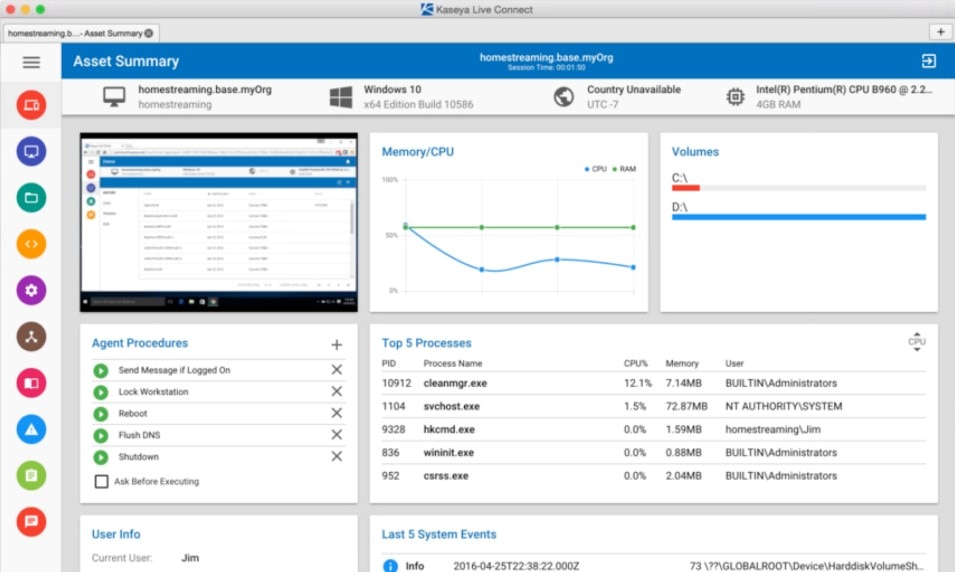
Kaseya VSA is a complete remote monitoring and network management tool with remote control features for network devices, patch and update management, network monitoring, virus and malware scanning, and auditing and backup.
The patch management component of Kaseya VSA provides you with a complete overview of patch statuses for all relevant devices in your network and within your responsibility. It also includes tools to deploy patches and automate software maintenance.
You can view the patch status of your entire network in a single dashboard, which makes it easier to determine which applications need updates, and which are particularly vulnerable to attack. You can also use the Scan and Analysis feature to perform a complete scan of your network, whether on a regular schedule or on an as-needed basis, and to perform scans and updates automatically. If you want to stop all update and patch processing for a period, you can set “Blackout Windows” for the period in question.
One of the notable features of the Kaseya VSA patch management tool is its use of “Policy Profiles.” These profiles create rules you can standardize and scale to fit your network, with the capacity to approve, deny, or provide machine associations for all your updates. You can pre-design these rules and then apply them when you want to follow through with your updating processes. This can save you a lot of time and energy.
In addition to the Policy Profiles, “Override Profiles” allow you to block specific updates to groups of machines or deny a specific patch from being applied. Using a combination of Policy and Override Profiles, you can create a comprehensive system for updating and patch application.
Kaseya VSA works with WSUS when a device isn’t connected to a network, in which case it uses the WSUS .CAB data file. This .CAB file includes high-priority updates and service packs. The tool also links in with Windows automatic updates and can enable, disable, or set scheduling for these processes.
One of the main downsides of Kaseya VSA is it doesn’t provide pre-tested patches or patch testing capabilities. In addition, it doesn’t allow for the prioritization of patches, nor does it provide compliance management reporting. With these limitations in mind, Kaseya VSA is a good tool if you’re looking for basic patch management as part of a larger network monitoring solution.
PDQ Deploy is an alternative Windows update tool made by the company formerly known as Admin Arsenal. The founders began working for other companies supporting the IBM Tivoli Management Framework and Microsoft SCCM. They went on to create tools to suit smaller and medium-sized businesses, and then expanded again to the enterprise level.
PDQ Deploy is a software deployment tool designed to keep Windows PCs up to date with minimal effort. It can deploy any Windows patch or application through SCCM, to all your Windows PCs at the same time. These deployments can install or uninstall patches or programs, reboot PCs, execute scripts, tell a PC to sleep, or copy files and send messages and instructions. Once your deployment is finished, the tool will generate a report on the deployment and execution.
You can set a schedule for your updates to be downloaded and automatically applied, and if you use PDQ Deploy with PDQ Inventory, you can set all your updates and patches to continue automatically when a previously asleep device comes online again. You can also set up PDQ Inventory so once a deployment has occurred, the tool will automatically scan your network and update the inventory for you. Considering what it adds in terms of patch management it’s a little inconvenient that PDQ Inventory doesn’t come along with PDQ Deploy.
With PDQ Deploy, you can choose to write and execute your own scripts to control the patching process, including scripts in .vbs, reg, .bat, and .ps1 formats. Alternatively, you can simply use the default functionality. The tool includes a library of 175 third-party applications you can download easily, and it integrates the updates for those applications, so when an update is released it becomes available to you as soon as possible. PDQ Deploy also lets you receive email notifications, so you can keep track of your deployments and whether they were successful. Although the list is extensive, some widely used programs are for some reason not included.
You can try out PDQ Deploy free for 14 days or download a free version with limited features. The enterprise license is available on a per-admin basis. Purchasing both PDQ Deploy and PDQ Inventory will double the cost per admin.
PatchLink by Ivanti is an alternative WSUS patch management and application tool with a focus on security at the enterprise level. Ivanti was formed in 2017 from a merger of two smaller companies, one of which was formerly owned by IBM. Their software is well known, especially when it comes to their offerings in the areas of patch management and enterprise service management.
The PatchLink tool is designed to prevent security vulnerabilities from arising in your network due to buggy software or unpatched issues. It has useful core features, and it integrates well with SCCM, providing a simpler way to patch both Windows and third-party apps through the SCCM console. Using PatchLink, you’ll eliminate many of the steps typically involved in patching apps from third parties.
The patches available through Ivanti PatchLink are all pre-tested, which means you can apply them with confidence. You can also gain insights into the patching process through the tool’s SCCM reporting capabilities. In addition to SCCM, PatchLink links in with WSUS. It auto-detects WSUS updates and includes a dashboard in which you can view and manage all products published to WSUS.
Ivanti PatchLink provides a searchable view of available patches, and includes smart filtering based on criteria including vendor, product, information assurance vulnerability alert number, and so on. The filtering feature makes it much easier to quickly find patches and determine whether they’ve been applied to your systems. Moreover, you can customize any of these patches if modifications are needed to comply with your company’s policies.
Patches can be checked for, downloaded, added to new or existing software update groups, and published automatically. You can also publish patch metadata for compliance, audit, or pre-deployment screening purposes, so you have fine-grained information on the entire patching process.
A free demo of PatchLink is available on request. The company isn’t as transparent about their pricing as some of the others on this list; for a quote, you’ll need to make a request through their website.
BatchPatch was created by a small company called Cocobolo Software. They have been around since 2011, and BatchPatch is the only software they make.
BatchPatch is a high-quality tool with a single console from which you can download and apply patches and updates to many remote Windows computers simultaneously. You can elect to install all available updates or pick out which specific ones you want to be applied. You can also determine which updates you want installed based on how they’re grouped—as a service pack, driver or tool, critical update, and so on. Being able to choose patches based on these categories can help you refine and prioritize your process, so only the most important patches are applied during critical times, and less important patches can be applied during downtime.
You can use BatchPatch in conjunction with WSUS, Windows Update, or Microsoft Update. It also includes an offline mode for updates needing to be applied to computers without internet access.
The tool includes an integrated task scheduler, so you can launch any of your patching jobs or tasks at the time of your choosing. You can schedule jobs to take place sequentially on remote hosts, either by setting one patch to install after another, or by setting up scripts to run before or after a device has been rebooted. This helps you to plan for periods when you might not be immediately available but need a series of tasks to take place. You can also easily execute remote scripts with BatchPatch, to push configuration changes or apply settings to remote devices.
BatchPatch provides a yearly license with support, based on a pricing “per user” model. You can try out the evaluation model for free, but it only works with up to four simultaneous target hosts in the grid.
Tools for Managed Service Providers: N-central and RMM
The above tools can be a good fit for a variety of use cases and industries. However, if you’re a managed service provider or similar, you might benefit from a tool that’s optimized specifically for your needs.
N-central is a patch management solution that can deploy Windows 10 updates through a quick and simple approval process. Plus, it includes automation and reporting functionality, along with a slew of other features to help you manage updates across many unique client sites.
Remote Monitoring & Management (RMM) comes from the same family of tools, and also provides a full suite of patch management tools. It supports updates on multiple OSs, along with a wide variety of software. RMM is a great alternative if your client base isn’t running exclusively on Windows.
Choosing a WSUS Alternative
In this article I’ve covered the best alternatives to WSUS, whether you’re looking for a patch management solution to complement WSUS and SCCM or a tool to act as a complete Microsoft WSUS replacement.
The market is largely lacking in good free WSUS alternatives, but free trials let you try out most of the tools on this list. My pick for a free solution is the SolarWinds WSUS client diagnostic tool, which has great functionality at a basic level. If your business is small or medium-sized, you may find this free WSUS alternative is sufficient. However, if you use many third-party applications, investing in an enterprise-level patch management tool will save you a great deal of time and energy.
At the enterprise level, you need to be handling your updates and patches in a controlled manner, for the purposes of security, compliance, and performance discussed above. Among other concerns, you need to be much more careful about managing bandwidth and timing updates appropriately, or risk slowing down your entire network at an inconvenient time. Implementing a quality tool like SolarWinds Patch Manager is the best way to take control over the patch management process.


