Best Network Monitoring Software
Knowing what’s happening in your network infrastructure is essential so you can stay on top of issues before they affect users. With the right network monitoring tools, you can track, analyze, and optimize your network’s health and performance and get real-time visibility into traffic, device conditions, and overall infrastructure performance.
This post will explore the seven best network monitoring tools and guide you through the nitty-gritty of network performance monitoring.
Best Network Monitoring Software
1. SolarWinds Observability (Free Trial)
What Is Network Monitoring, and Why Is It Important?
What Is Network Monitoring Software, and How Does It Work?
Categories of Network Monitoring Tools
How Can Network Monitoring Software Help Optimize Networks and Troubleshoot Issues?
What Types of Network Devices Can Be Discovered and Monitored?
Most Important Capabilities of Top Network Monitoring Solutions
Best Practices for Network Monitoring
How to Choose Network Monitoring Software for Your Company
1. SolarWinds Observability (Free Trial)
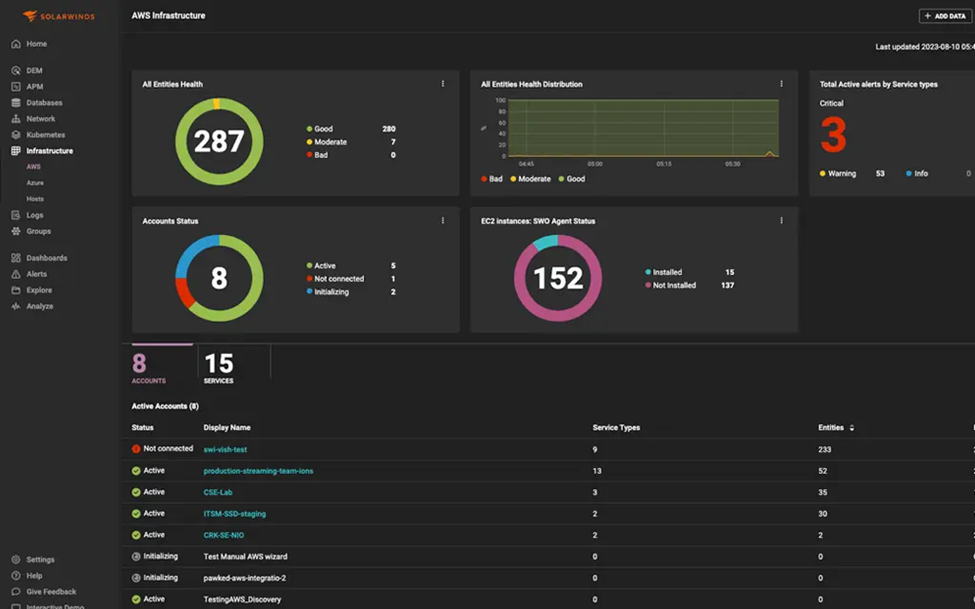
©2024 SolarWinds Worldwide, LLC. All rights reserved.
SolarWinds Observability is a comprehensive network monitoring and management platform, which can be deployed as a self-hosted or SaaS-based solution. It combines traditional network monitoring with cloud-native observability practices, allowing IT teams to monitor, manage, and optimize complex hybrid environments. SolarWinds offerings include real-time monitoring, advanced analytics, and integrated security monitoring. Organizations can gain a holistic view of their IT infrastructure by leveraging network performance metrics and cloud observability data. This approach ensures effective monitoring of legacy and modern systems, making it particularly beneficial for businesses transitioning to the cloud. SolarWinds Observability tools include robust integration capabilities with various cloud providers, making them a leading company for maintaining performance and security across diverse environments.
- Provides comprehensive visibility across hybrid environments
- Integrates traditional monitoring with cloud observability
- Can be deployed as self-hosted or SaaS
- Enhances security and compliance monitoring
- Scales to support complex IT setups
2. PRTG
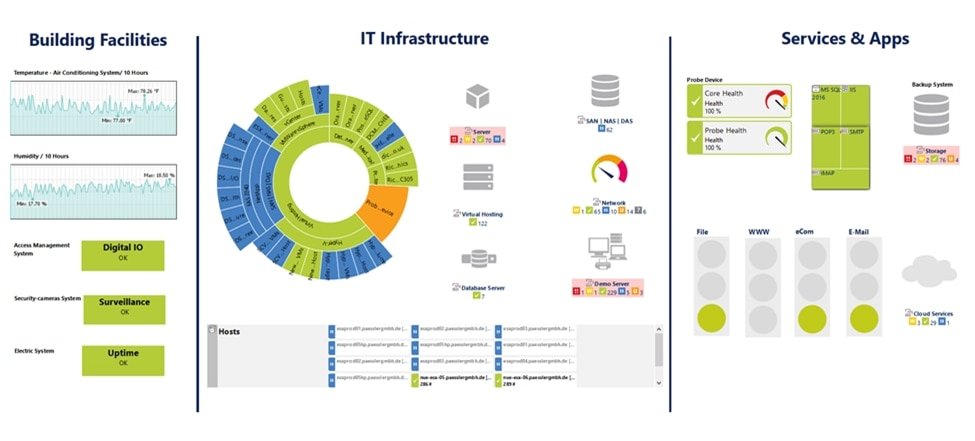
©2024 Paessler AG
PRTG Network Monitor is a network monitoring solution known for its ease of use and flexibility. It monitors IT infrastructure systems, devices, traffic, and applications by gathering data from network devices using various technologies, including SNMP, WMI, and NetFlow. It offers auto-discovery features that can map out your network and begin monitoring quickly. It provides a customizable dashboard interface, allowing users to create maps, charts, and custom views of their network. PRTG includes sensors for various aspects of IT infrastructure, including hardware health, bandwidth usage, and application performance. It offers on-premises and cloud-hosted options, making it suitable for different deployment preferences.
- Easy to set up and use
- Flexible licensing model based on sensors
- Good visualization tools
- Mobile apps for on-the-go monitoring
3. OpManager
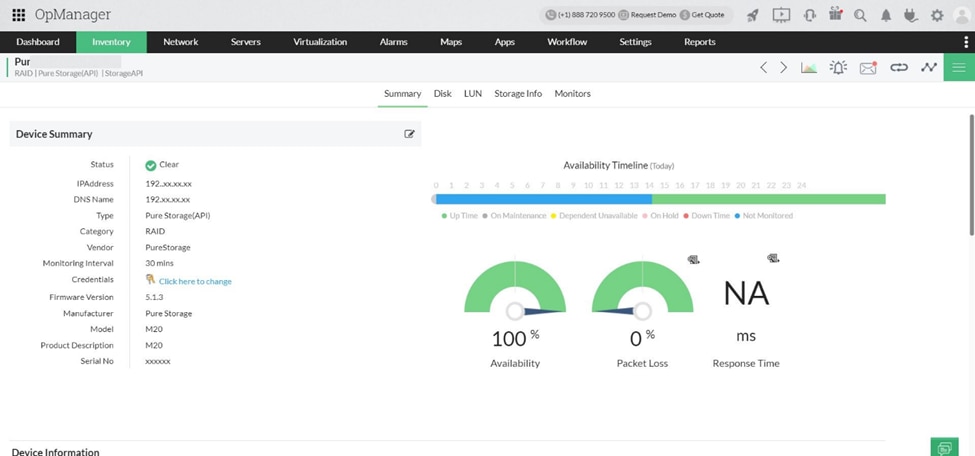
2024 Zoho Corporation Pvt. Ltd. All rights reserved.
ManageEngine OpManager is a network monitoring tool that offers end-to-end visibility into network performance. It’s designed to help IT teams proactively monitor and troubleshoot network issues.
OpManager provides real-time monitoring of network devices, servers, and applications. It offers automatic discovery and mapping of network devices, visually representing the network topology. OpManager offers features for bandwidth monitoring, configuration management, and IP address management. OpManager also provides detailed performance metrics, customizable dashboards, and a variety of prebuilt and custom reports. It supports physical and virtual environments and includes tools for monitoring cloud services.
- Comprehensive feature set covering various aspects of network management
- User-friendly interface with customizable dashboards
- Alerting and notification system
- Integrates well with other ManageEngine products
4. Nagios XI
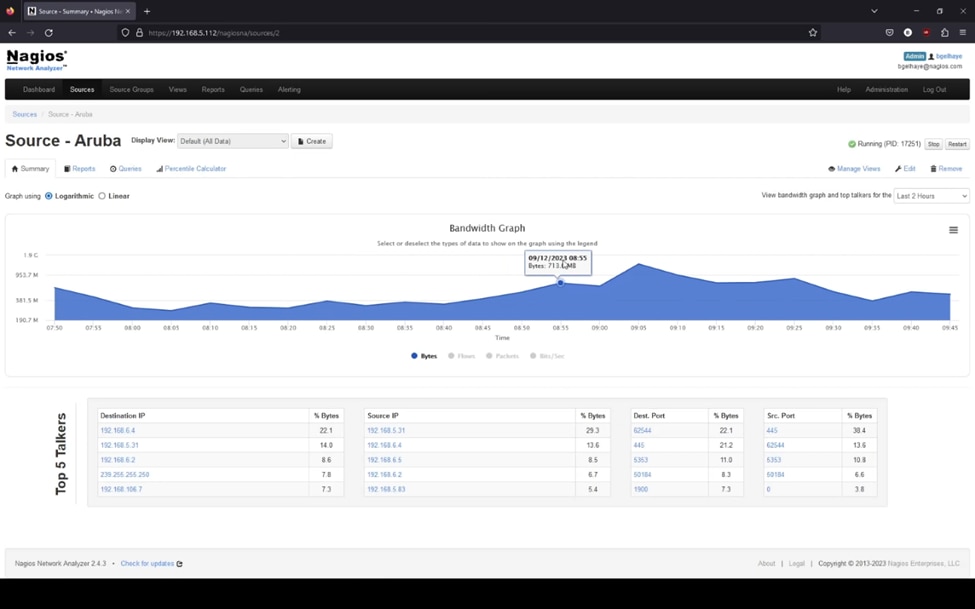
Copyright © 2009-2024 Nagios Enterprises, LLC. All rights reserved
Nagios XI is enterprise network monitoring software known for its flexibility and extensibility. It’s built on the open-source Nagios Core but offers additional features and a user-friendly interface. Its capabilities enable comprehensive monitoring of networks, systems, and applications. It offers a web-based interface with customizable dashboards and views. Nagios XI offers network topology mapping, performance graphing, and capacity planning tools. Nagios XI is highly extensible, with a large library of plugins for monitoring various devices and services. It supports both agent-based and agentless monitoring, providing flexibility in deployment. also It also offers advanced reporting features and the ability to create custom reports.
- Highly customizable and extensible
- Extensive community and plugin ecosystem
- Alerting and notification capabilities
- Supports both agent-based and agentless monitoring
5. LogicMonitor
© Copyright 2024 LogicMonitor Inc.
LogicMonitor is cloud network monitoring software with a full-stack monitoring platform that provides visibility into networks, servers, cloud services, and applications. It’s designed to offer automated monitoring for hybrid IT environments.
It uses an agentless approach to discover and monitor devices across on-premises, cloud, and hybrid environments. It offers preconfigured monitoring templates for various devices and technologies, enabling quick deployment. The platform provides real-time performance metrics, customizable dashboards, and robust alerting capabilities. LogicMonitor also includes features for log analytics, configuration management, and AIOps, helping predict and prevent IT issues before they impact users.
- Cloud-based with easy deployment and scalability
- Monitoring with auto-discovery
- Analytics and reporting
- Integration capabilities
6. Datadog
© Datadog 2024
Datadog is a monitoring and analytics platform designed for cloud-scale applications. It provides monitoring across on-premises, cloud, and hybrid environments.
Datadog’s platform offers a unified view of metrics, traces, and logs across the IT stack. It monitors networks, servers, databases, applications, and cloud services. It offers service discovery, customizable dashboards, and powerful analytics tools. Datadog’s cloud observability capabilities allow teams to monitor traditional and cloud-native infrastructure from a single platform. It also offers features like anomaly detection, forecasting, and correlation analysis.
- Monitoring for modern, distributed environments
- Integration capabilities with a wide range of technologies
- Analytics and visualization tools
- Regular updates with new features and integrations
- Support for cloud-native and containerized environments
What Is Network Monitoring, and Why Is It Important?
Network monitoring is the consistent observation of a computer network for issues or failures using various network monitoring solutions. It’s about monitoring a network for any security issues and making sure it performs optimally. Network monitors track network components like routers, switches, firewalls, servers, and activities. The aim is to detect and respond to outages and discrepancies and maintain security. Some specific things that are typically monitored include network traffic, user activities, and bandwidth usage. You can identify bottlenecks that help you filter and narrow down potential issues when troubleshooting by keeping track of network traffic.
Network monitoring is essential for several reasons. Early problem detection helps minimize downtime and service interruptions. It can also identify unnecessary resource usage, helping you optimize spending.
What Is Network Monitoring Software, and How Does It Work?
Network monitoring software is a specialized solution that identifies, analyzes, and observes network components. It tracks different aspects of the network infrastructure, including health, security, and performance, by providing insights via logging and sending alerts based on defined thresholds.
Although different network monitoring tools may vary in their operations, here’s how most work:
Device Discovery and Mapping
First, the network monitoring software scans the network for all connected devices, such as servers, routers, switches, and firewalls. It uses protocols like SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol) or ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol) to discover and gather information about devices. After finding them, it creates a topology to show the connection between different components.
Data Collection
The next step is collecting performance metrics from network devices, including CPU, memory, bandwidth, and disk space usage. Further, it collects and analyzes logs from network devices, which can provide detailed information about events, errors, and security incidents.
Visualization
Network monitoring software offers a customizable dashboard to give you a general outlook on your network’s performance. It shows the network’s health, which can be modified according to your needs. You can also generate reports on uptime, security incidents, and performance.
Alerting
With alerting, you can set predefined thresholds for various metrics, like network latency or downtime. Network monitoring software triggers alerts and notifies the administrators via email, SMS, or other communication channels when a threshold is exceeded.
Monitoring
Apart from collecting the metrics, network monitoring software monitors network traffic to analyze the data flow across the network. This helps identify traffic patterns, potential bottlenecks, and unusual activity. The software continuously monitors the network in real-time, providing up-to-date information on its status and health.
Automation
Network monitoring tools can automate tasks such as restarting a service, running a script, or adjusting network settings depending on different conditions.
Categories of Network Monitoring Tools
Now that you know what network monitoring software tools are, we’ll look at some different categories:
Performance Monitoring
Network performance monitoring software tracks the various performance metrics of network devices and systems to ensure they operate efficiently. It monitors metrics that show the efficiency and health of a network, such as CPU usage, memory utilization, disk space, and network bandwidth.
Performance monitoring allows IT teams to optimize the network, maintain high-performance levels, prevent outages, and ensure effective resource utilization.
Availability Monitoring
This category of network monitoring tool checks whether network devices, services, and applications are online and accessible. It also ensures that critical infrastructure components like servers, routers, and switches are operational and that network services are reachable by continuously sending ping requests to check availability.
If a critical server or service goes down, it can disrupt operations, lead to data loss, and cause financial loss. Availability monitoring helps detect outages or failures quickly, allowing for prompt response and minimizing downtime.
Traffic Monitoring
Another category of network monitoring tool tracks traffic. It does so by analyzing the data flow within a network. It focuses on understanding how data is routed through the network, identifying congestion sources, and ensuring traffic flows efficiently.
Traffic monitoring helps identify unusual traffic patterns, such as a distributed denial of service (DDoS) attack. By understanding traffic patterns in your network, you can manage bandwidth allocation, ensuring critical applications have sufficient resources.
Security Monitoring
Network monitoring tools monitor network activities to detect and respond to potential security threats, such as unauthorized access, malware, and data breaches. These tools monitor suspicious activities, detect intrusion, and make sure the network adheres to security policies and compliance standards.
These tools can monitor and analyze firewall, router, and server logs to detect unusual activities. They also regularly scan the network for vulnerabilities that attackers could exploit.
How Can Network Monitoring Software Help Optimize Networks and Troubleshoot Issues?
When you utilize network monitoring tools and software, you can see what’s happening in your entire network infrastructure. Here are some ways network monitoring helps you optimize and troubleshoot issues:
- Helps predict future network usage trends by analyzing historical data and traffic patterns
- Allocates bandwidth more effectively and prioritizes critical applications by identifying which applications or devices consume the most bandwidth
- Identifies underutilized devices or connections by tracking resource utilization across the network
- Quickly pinpoints where issues like packet loss or latency are occurring by mapping out the entire network topology and monitoring the status of each link
- Analyzes historical data to identify recurring issues or trends that may lead to future problems
What Types of Network Devices Can Be Discovered and Monitored?
A network monitoring tool should discover and monitor several devices, including the following:
Routers
Routers are devices that forward data packets between computer networks. They direct traffic on the internet by determining the best path for data to travel from one network to another.
Switches
Switches connect devices within a single network, allowing them to communicate by forwarding data to the appropriate device within the network.
Firewalls
Firewalls are security devices that monitor and control incoming and outgoing network traffic based on predetermined security rules. They’re a barrier between a trusted internal network and untrusted external networks.
Wireless Access Points
Wireless access points (WAPs) provide wireless network connectivity to devices within a specific area, allowing them to connect to the wired network. Using wireless network monitoring software, you can track signal strength and coverage.
VoIP Systems
Voice over IP (VoIP) systems enable voice communication over IP networks, replacing traditional telephone systems with internet-based communication.
IoT Devices
Internet of Things (IoT) devices collect and exchange data, ranging from intelligent sensors and thermostats to industrial machines and healthcare equipment.
Most Important Capabilities of Top Network Monitoring Solutions
For a network monitoring tool or software to be considered among the top solutions, it must have the following capabilities:
Discovery
Discovery is the process by which a network monitoring solution identifies all the devices, services, and connections within a network. This includes routers, switches, firewalls, servers, endpoints, and any other devices that communicate on the network.
Scalability
Scalability looks at the ability of the network monitoring solution to grow and adapt as the network expands. This is especially important for large enterprises and organizations with rapidly growing networks. For example, can the network and server monitoring software add more monitoring nodes or sensors as needed? Can it handle more devices and larger volumes of data without performance degradation? A scalable network monitoring solution ensures that the monitoring system can keep up as the network grows.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis involves identifying the root cause of network issues with performance, connectivity, and security. This is critical for maintaining network health and minimizing downtime. Network performance monitoring software can automatically analyze symptoms and trace them back to the root cause, such as a failing device or misconfigured network settings. Diagnostics help prevent issues that may threaten the performance and integrity of a network.
Analysis
Analysis involves processing and interpreting the data collected by the monitoring system to gain insights into network performance, usage patterns, and potential issues. The software analyzes bandwidth usage, latency, packet loss, and device performance to identify trends and anomalies. This analysis provides valuable information that helps improve network performance and plan for future growth or upgrades.
Alerting
Alerting allows the network monitoring system to notify administrators about issues as they arise, allowing immediate action. You can set up custom alerts based on specific metrics, conditions, or device types where you define thresholds that notify you when they’re reached. The network monitoring tool can reach you via email, SMS, or push notifications. These alerts are helpful because they allow quick remediation and minimize network downtime.
Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting involves the steps taken to diagnose, resolve, and prevent network issues. It’s a critical function that ensures the network remains operational and efficient. Network monitoring systems should offer step-by-step guidance or automated scripts to help resolve common issues, making troubleshooting faster and more efficient. Additionally, they should provide access to logs that you can use to track and identify potential problems.
Best Practices for Network Monitoring
To ensure that you’re making the most out of network monitoring, follow these practices:
- Select the right monitoring tools.
- Choose network monitoring solutions based on your requirements, considering scalability, integration capabilities, and ease of use.
- Make sure your monitoring solution delivers visibility throughout the network, including on-premises, cloud, and hybrid environments.
- Configure the monitoring system to detect potential issues before they degrade network performance or create downtime.
- Configure alerts to notify the right people at the right time based on the severity of the problem.
- Periodically review and adjust monitoring configurations to reflect network changes, such as the addition of new devices or changes in traffic patterns.
- Combine network performance monitoring with security monitoring to ensure a comprehensive approach to network health.
- Ensure the monitoring system is resilient, with fail-over mechanisms and redundant configurations.
- Maintain detailed documentation of the monitoring setup and processes and ensure your IT team is trained to use the monitoring tools effectively.
Important Integrations
It’s not enough to have network monitoring alone. You’ll also want to integrate your monitoring tools with the following:
Cloud Service Providers
Integration with cloud platforms like AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud allows monitoring tools to monitor cloud-based resources, including virtual machines, databases, and network services.
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM)
Integrating SIEM solutions allows network monitoring data to be fed into security monitoring systems, providing a holistic view of performance and security events.
Application Performance Monitoring (APM)
By integrating with APM tools, network monitoring solutions correlate network performance with application performance, optimizing both.
How to Choose Network Monitoring Software for Your Company
Which network monitoring tool will work best for your company depends on your needs and specifications.
- Consider the size, scale, and complexity of your network. More complex networks may require more advanced monitoring features.
- Choose a solution that can grow with your network, accommodating more devices and higher data volumes as needed.
- Look for software or tools that offer multiple notification channels (e.g., email, SMS, push notifications) so that you’re alerted wherever you are.
- Decide whether you need an on-premises solution or if a cloud-based solution is preferable. If you have a hybrid environment, choose a solution that can monitor both.
- Before fully committing, test the software or tool in your network environment. Evaluate how well it meets your specific needs and how easy it is to deploy and use.
This post was written by Mercy Kibet. Mercy is a full-stack developer with a knack for learning and writing about new and intriguing tech stacks.
