Active Directory (AD) is one of the core pieces of Windows database environments. It provides authorization and authentication for computers, users, and groups, to enforce security policies across Windows operating systems. LDAP, or Lightweight Directory Access Protocol, is an integral part of how Active Directory functions. Understanding the role LDAP plays in the functioning of AD is essential to protecting your business from critical security issues.
This guide will define LDAP in the context of Active Directory, explain the importance of both for security, and set out best practices to follow when using AD, including the implementation of a monitoring and management tool like SolarWinds® Access Rights Manager (ARM).
What Is Active Directory LDAP?
Lightweight Directory Access Protocol (LDAP) is an application protocol for working with various directory services. In other words, while it’s supported by Active Directory, it’s also used with other services.
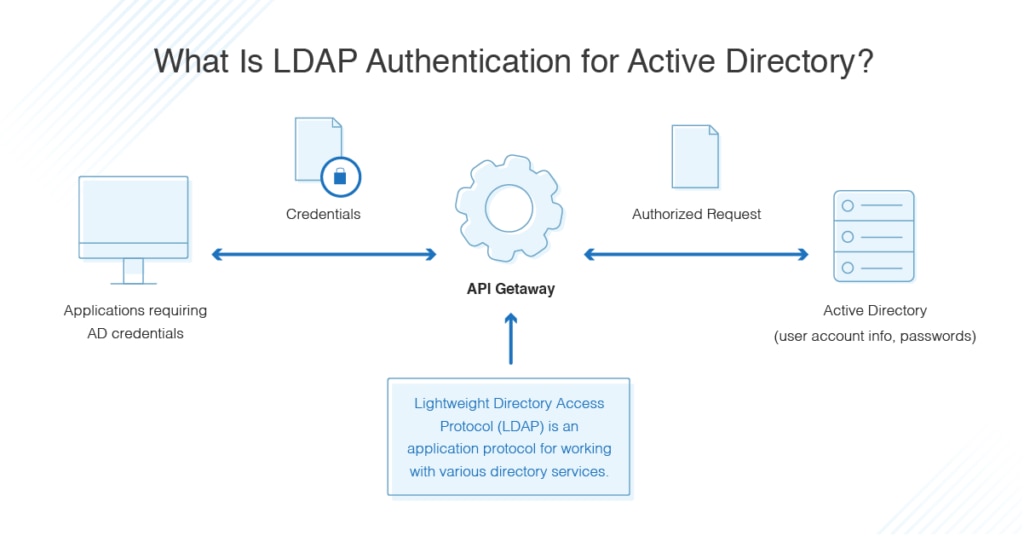
Directory services, such as Active Directory, store user and account information, and security information like passwords, and then allow the information to be shared with other devices on the network. LDAP is the language applications use to communicate with other servers also providing directory services. It’s essentially a way to “talk” to Active Directory and transmit messages between AD and other parts of your IT environment.
The way you begin an LDAP session is by connecting to an LDAP server, known as a Directory System Agent, which “listens” for LDAP requests. “Domain controller” is another name for the server responsible for security authentication requests. For users, domain control (DC) is the centerpiece of Active Directory. DC determines how AD provides authentication, stores user account information, and enforces the security policies you’ve applied across the domain controller or server.
How Does Active Directory Work With LDAP?
The next thing you need to understand is how AD LDAP authentication works. Essentially, you need to set up LDAP to authenticate credentials against Active Directory. The “BIND” operation is used to set the authentication state for an LDAP session in which the LDAP client connects to the server.
You have two options when it comes to performing LDAP authentication: simple and SASL.
- Simple authentication: This encompasses three possible approaches – anonymous authentication, unauthenticated authentication, and name/password authentication. In most cases, simple authentication essentially means a name and password are used to create a BIND request to the server for authentication.
- SASL authentication: The SASL (Simple Authentication and Security Layer) framework uses another authentication service—for example, Kerberos—to binds to the LDAP server, and then uses the authentication service to authenticate. This can provide enhanced security, as the separation of authentication methods from application protocols makes the directory less vulnerable in general.
By default, all LDAP authentication messages are sent in plain text, which can leave LDAP authentication processes open to security issues. To prevent this, you should be using a security measure such as encryption using TLS, or Transport Layer Security.
Once you have chosen your LDAP authentication method and have completed the process of LDAP integration with Active Directory, you can use the combination of these two systems with whatever application you want. This means you can use Active Directory to manage permissions for your application, files, groups, and so on, with LDAP as the messenger helping AD to integrate with the rest of your systems.
Make sure your Active Directory LDAP configuration settings are accurate at all times. This entails knowing whether authentication is enabled, whether you’re using simple or SASL authentication, whether authentication for FTP access is enabled, and whether user and group synchronization is enabled. Another factor you might want to consider is how your queries and search bases are set up; otherwise, you might be missing users and groups in the course of processes like scanning for security issues or performing checks prior to audits.
Why Are LDAP and Active Directory Important?
For managed services providers, it might be obvious why LDAP and Active Directory are so important, but if you’re new to this space, here’s why you need to think carefully about how to use them effectively.
Active Directory is part of the security layer for your IT systems, and LDAP is a core part of how AD works. This means both pieces are critical for keeping your IT environment secure.
Active Directory is the part of your system designed to provide a directory service for user management. It helps you manage and control all the devices on your network, including computers, printers, services, and mobile devices, and the users who engage with the devices. You can assign privileges to each user or group of users to allow them access to the objects (devices) or information contained in Active Directory.
Active Directory authentication is important because access to information in the directory can make or break system security, and directory services are essentially a phonebook for everything your organization holds in terms of information and devices.
The directory server and server LDAP integration are a critical result of these services functioning appropriately and securely. With LDAP, users can access the information they need in AD to do their jobs effectively. To configure LDAP correctly, you need to understand what authentication processes you need, how users will be searching the systems, and where your security and information needs lie.
Due to the critical role of Active Directory in your IT environment, it can be a target for hackers and malicious actors who want to breach your security systems. If a single high-level or high-access account is accessed, you risk the exposure of sensitive data such as files and information, or passwords for other accounts. LDAP is key to protection in Active Directory because it provides the authentication piece of the whole operation.
Active Directory Best Practices
Active Directory plays a vital role in the security systems of your IT environment. For this reason, when using AD, take care to adhere to the following best practices, for more details read our Ultimate Guide to Active Directory Best Practices:
- Ensure proper configuration. Take the configuration steps slowly and carefully, to make sure Active Directory is set up right in the first place. With proper configuration of your LDAP servers, you’ll cut down on the likelihood of an AD problem impacting your end users.
- Carefully configure AD groups. When setting up your Active Directory groups, be sure to separate them based on role or the access they should have and keep these groups up to date. For example, if someone moves into a new role, their group designation should be updated. Managing these aspects of AD helps to prevent unauthorized access, so your system stays secure.
- Follow the principle of least access. When it comes to Active Directory, setting up each user or group with the least access necessary to do their job or execute their role is important. The more access any one group or user has, the higher the chance the access can be abused. In other words, the less access you give each user and group, the safer you keep your systems as a whole.
- Make use of tools. One important step you can take to make sure your Active Directory is set up correctly is to use high-quality professional tools. A centralized solution like SolarWinds Access Rights Manager will help you to effectively manage your Active Directory configurations and permissions.
ARM includes several features specifically designed for managing Active Directory, including tools to simplify Active Directory delegation, tools for group management, and permissions reporting. Additionally, the Active Directory Auditing Tool helps ensure security and compliance. These features make sure your AD setup is both secure and efficient.
Whether you choose ARM or another tool, it’s vital you test it thoroughly in a portion of your business environment before rolling it out to your entire IT system. SolarWinds allows you to do this by downloading a 30-day free trial of ARM.
In addition, perform regular updates, generate Active Directory permissions reports, and check to ensure your software and tools are up to date and working effectively for your business. - Undertake regular reviews. Along the same lines, you should also be performing regular reviews of your Active Directory and LDAP authentication setup, regardless of whether you’re using a tool or not. You need to ensure there are no configuration changes capable of creating a security risk or an error.
Managing LDAP and Active Directory
LDAP is a critical part of the functioning of Active Directory, as it communicates all the messages between AD and the rest of your IT environment. For this reason, implementing the correct configuration and authentication settings is vital to both the security and the day-to-day functioning of your IT systems. By following the above processes, including adopting a tool like SolarWinds ARM to monitor and manage your AD user access rights, you can make sure your Active Directory is set up correctly with LDAP authentication, and you’re using it in a secure and efficient way.
