MySQL is a popular open-source relational database management system and knowing how to optimize it is essential. Slow database performance can severely affect all your applications and users; a single poorly designed SQL query can have a big impact.
Optimizing your MySQL database isn’t a simple process, but it’s vital for maintaining application performance and service delivery. In this guide, we’ll look at 10 tips for how to optimize your MySQL database performance—from familiarizing yourself with your workload to implementing software such as SolarWinds® Observability.
- Understand Your Workload
- Optimize Queries
- Don’t Use MySQL as a Queue
- Monitor the Fundamental Resources
- Filter Results
- Optimize Subqueries
- Recognize Scalability Problems
- Query the Cache
- Check Pagination Queries
- Automate Configuration
There are several tips for optimizing MySQL database performance; some of these can get technical, while others are more high level. The following are my “biggest bang for your buck” approaches, but there are many other, smaller optimizations you can also look into if you want to get really technical.
Tip 1: Understand Your Workload
First, it’s important to understand how your MySQL database is working, so you can baseline and profile what you’re currently dealing with. Without accurate baselines and workload profiling, it’s hard to pinpoint where you could potentially employ optimization measures. By looking at your current workload, you can see which queries are the most expensive.
The easiest way to profile or baseline your database performance is to use a tool, such as those covered under tip 10.
Tip 2: Optimize Queries
The next thing you need to do is optimize your SQL queries. As I noted before, one rogue SQL query can become expensive fast and can majorly impact your entire operation. One of the first things you can do to optimize your queries is to focus on indexing.
Indexes are used to help operations find data more quickly in tables stored in the database. You can help your index be more efficient by indexing all your predicates by WHERE, JOIN, ORDER BY, and GROUP BY clauses. This allows the indexes to be moved through more quickly when someone wants to find information.
Tip 3: Don’t Use MySQL as a Queue
Next, make sure you’re not using MySQL as a queue, where you set up operations to be carried out one after the other. This can slow things down in any circumstance where operations could have run in parallel. It can also slow things down when, for example, some tasks are waiting for others to be completed, in which case your table may contain a mixture of work in progress and completed tasks or historical data. This makes the database less efficient.
Tip 4: Monitor the Fundamental Resources
For your database to function well, you need to monitor the four indispensable resources that allow it to operate:
- CPU
- Memory
- Disk
- Network
If your memory is running low, or if your disk is full, your database will be impacted no matter how optimized it is.
Tip 5: Filter Results
If you’re looking for something specific or want to process a certain kind of data, a good way to approach it is to do the less costly and precise work first, and then drill down into more precise queries later. This way, you can ensure you aren’t running expensive functions on large sets of data when it’s unnecessary.
Tip 6: Optimize Subqueries
When it comes to optimizing subqueries, opt for a join where possible. In newer versions of MySQL, subqueries may already be optimized, so check whether this is necessary.
Tip 7: Recognize Scalability Problems
Some systems will scale better than others. If you have any serialized processes, this will limit scalability simply by adding more processes that have to wait for others. You also need to make sure you avoid cross talk. Keep everything parallel and unlocked as much as possible.
Tip 8: Query the Cache
Caching can improve performance by allowing data to be stored for faster access, and the MySQL query cache is no exception. If a query is stored and then an identical query is received in the future, it will return results much faster. You can maximize MySQL cache optimization by caching the content.
Tip 9: Check Pagination Queries
If you are using applications that paginate, sometimes they will group and sort in ways that don’t or can’t use indexes. This creates a lot of work for the server. You can create optimizations by only showing the link to the next page, rather than links to all available pages.
Tip 10: Automate Configuration
For automating the performance tuning and configuration of your MySQL database, I recommend SolarWinds Observability SaaS (formerly known as SolarWinds Observability). It is a cloud-based solution, offering a comprehensive and user-friendly web interface.
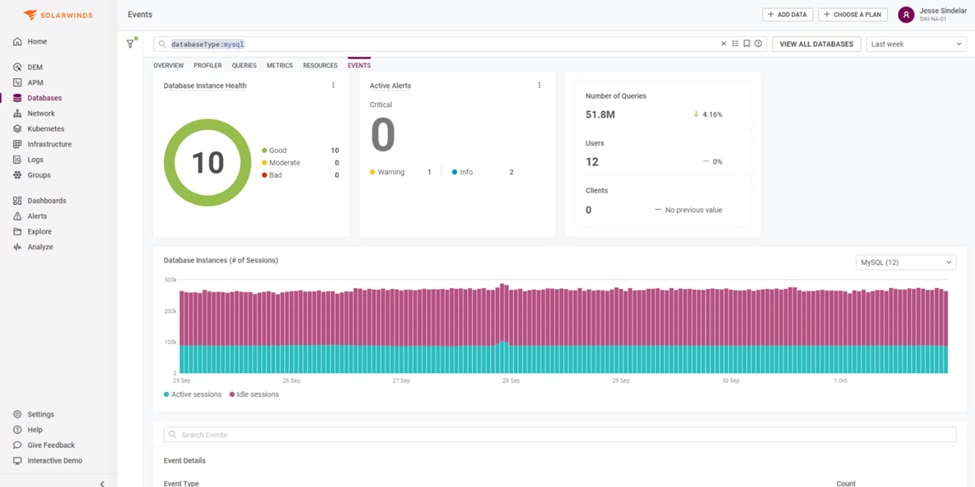
It’s designed for administrators to monitor performance effectively and pinpoint issues within the database. Continuous data collection is one of the tool’s strengths, simplifying the process of identifying the root cause of performance bottlenecks. With SolarWinds Observability SaaS (formerly known as SolarWinds Observability), you can engage in robust performance optimization and configuration, monitoring aspects like SQL Server performance, application wait times, client machine activities, and user interactions. It provides detailed insights into the four fundamental resources – CPU, memory, disk, and network – mentioned earlier, allowing for a holistic view of your database’s health. . SolarWinds Observability SaaS (formerly known as SolarWinds Observability) also includes anomaly detection powered by machine learning, enabling proactive identification of potential issues. Its workload trend analysis and optimization change tracking are invaluable for determining the effectiveness of any adjustments made. For those looking to streamline their database performance tuning process, you can try SolarWinds Observability SaaS (formerly known as SolarWinds Observability) free for 30 days, allowing you to optimize your MySQL database performance within the broader context of your IT infrastructure.

Optimizing MySQL Through Performance Tuning
Performance tuning is an important part of maintaining a MySQL database. In addition to familiarizing yourself with your database and taking manual steps to optimize performance, you will greatly benefit from the use of a tool to automate necessary processes. For admins seeking on-premises software, I recommend Database Performance Analyzer, while those looking for a SaaS solution should consider above mentioned SolarWinds Observability SaaS (formerly known as SolarWinds Observability).
By taking the above steps, you can ensure your MySQL database performance is optimized, allowing you to get work done more efficiently and ensure your business services and applications remain available.


