Your organization’s IT environment is intricate, and as you increase operations your network grows more complex. The more jobs your network performs, the more difficult it becomes to streamline tasks and ensure seamless user experiences. But no matter how elaborate your business’s topology becomes, it will always rely on exceptional hardware performance.
Virtual machines, or VMs, run multiple operating systems simultaneously from the same piece of hardware, called a VM host or core. A VM acts as a stand-alone system with its own memory, storage, interfaces, and its own virtual CPU (vCPU) known as a VM processor. Virtual machine processors take up some storage space on a VM’s core or host to perform jobs and run applications.
Since they take up little physical space but operate as if existing on fully-fledged hardware, virtual machine processors are often fighting for VM resources. Correctly allocating resources between various VMs present in your IT infrastructure will ensure fair and efficient virtual machine resource allocation. Maintaining a healthy balance of virtual machine resources will optimize individual VM capabilities, thereby improving your overall network performance.
To make sure the work of analyzing the performance of a virtual machine environment doesn’t become a monotonous, difficult and mistake prone task, I can suggest one of the tools available on the market to support administrators. In my opinion, an experienced IT staff and beginner administrators will be interested in this type of tools for monitoring and analyzing virtual machines. So, if you’re looking for a proven tool that:
- Allows you to monitor and control your virtual environment – both on your own servers and those based in the cloud
- Helps detect and resolve performance issues in virtual machine – such as misallocated resources or accumulated VMDK files destined for deletion
- It has a customizable dashboard – you monitor what’s important to you, set your own alarms notifying you of events relevant to your work in optimizing the virtual machine environment
I recommend using a tool such as SolarWinds® Virtualization Manager. Not only is VMAN designed to pinpoint particularly troublesome VM processors and low-performing VMs, but it also enables you to manage virtual allocation and the overall health of your network’s virtual machines. You can access a 30-day free trial.
What Is Virtual Machine Resource Allocation?
Before we dive into VM resource allocation, let’s go over the general definition and purpose of resource allocation in IT administration. Resource allocation describes the process of figuring out the best way to distribute limited resources between multiple applications. Virtual machine resource allocation is this same task: determining how to best divide VM resources between the VMs present in your network. Effective resource allocation will ensure all VMs complete jobs successfully and without draining excessive resources.
Virtual allocation is the act of provisioning virtual machine processors onto physical hosts or cores, such as your CPU, to increase networking facilities and opportunities. Enacting proper virtual machine resource allocation will help you distribute operations fairly among VMs used for virtual allocation. Virtual allocation may seem like a dream come true, but keep in mind virtual machine resource allocation often leads to optimization problems — more VM processors means more connections within your network, which increases the number of simultaneously occurring operations. The more operations going on at once, the higher your chances of latency, bottlenecks, and other performance issues.
Now, the general rule is you shouldn’t over-allocate your virtual machine processors. This means you should maintain a 1:1 ratio between your virtual machine processor and its host or core. It’s recommended to only have one VM processor per host because if you over-subscribe virtual machine processors to a single core, events could be stalled or delayed to the point of extreme frustration and user dissatisfaction. But it’s unrealistic to maintain you should never over-allocate your VM resources, or to pretend IT administrators don’t over-allocate their virtual machine processors.
The truth is, you can add as many virtual machine processors as you like to a host. However, it’s best to start small to prevent overloading your network. A good general rule for bringing virtual allocation into your IT infrastructure is to start at a 2:1 ratio and work your way up in small increments — for example, start at 2:1 then move to 4:1, to 8:1, to 12:1, and so on. If you monitor for the potential consequences of virtual machine resource allocation, such as latency and bottlenecks, you can indefinitely increase your virtual machine resource distribution.
Oftentimes, IT administrators will enlist the help of a hypervisor to run virtual machines and aid with virtual machine resource allocation. Hypervisors manage processes using threads, which are sequences of CPU instructions. While you cannot permanently assign hypervisors to a particular host, you can assign specific threads to specific cores for more customization. Hyper-V is one common hypervisor used to manage virtual machine resource allocation. Like VM resource allocation, Hyper-V virtual processor allocation can still yield delayed or lost operations and other performance issues. But using Hyper-V or any other hypervisor will certainly help you stay on top of your virtual machine resource distribution and individual VM performance.
Tips for Virtual Machine Resource Dispersion and Allocation
There are a few tips and tricks you can follow to maximize virtual allocation and optimize virtual machine resource allocation. This will enable your network to support many tasks simultaneously while still ensuring they run as efficiently as possible.
1. Establish baselines
Baselines are generated by collecting data on virtual machine resource workloads, tasks, and application use over time to juxtapose current performance metrics to previous performance metrics of similar qualities. This will help you understand how individual virtual machines are performing at a particular moment as compared to previously, and how effective your virtual partitioning process is currently versus how it was in the past. Monitoring your virtual machine resource allocation over time enables you to understand your network capabilities, discover best practices and opportunities for growth, and anticipate the future of your virtual allocation infrastructure.
One example of forming baselines, also called benchmarking, is to evaluate virtual machine resource use throughout the day. Oftentimes when performing virtual allocation, there are bursts of activity at the beginning and end of the work day as end users sign in and out of their machines. This is commonly known as a boot storm. Boot storms usually result in delays during the morning and evening but acceptable performance throughout the rest of the day. Using baselines allows you to take boot storms into consideration when monitoring virtual allocation activity, so high latency periods at these times of day don’t cause problems.
2. Constantly monitor virtual allocation
To ensure optimal virtual machine resource allocation, you should consistently check on the performance of your VMs and your VM resources. This will keep you up to date on how many VM resources are in use at a given time, along with which virtual machine they’re allocated to. Virtual machine resource allocation can change in an instant, making it easy to accidentally waste or mismanage VM resources.
Persistent virtual machine resource monitoring will also prevent VM resource allocation issues from initially flying under the radar. When undiscovered or left alone, problems relating to virtual machine resource distribution can develop into massive performance issues yielding detrimental latency and bottlenecks, loss of data, and VM corruption. Make sure you’re regularly monitoring the VMs allocated to cores and hosts in your network, and the overall allocation of VM resources between virtual machines.
3. Invest in a virtual machine resource monitoring tool
Virtual machine resource allocation tools are designed to help uncover and understand critical information about your VM resources, how they’re allocated and used, the health and functionality of your virtual machines and hypervisors themselves, and other essential virtual allocation metrics. Awareness of important data regarding your VM environment will help you maintain an efficient, healthy, and high-performing IT infrastructure to transmit data quickly and reliably. Virtual machine resource monitoring software could enable faster turnaround time, ensure service reliability, and minimize human error occurring during manual hypervisor and VM monitoring. Virtual machine resource tools can also increase the availability of your VM resources and overall IT environment, resulting in increased network speed and disk space.
Virtual machine resource allocation monitoring tools can also allow you to save money in the long run. Because of their efficiency and reliability, software designed to monitor VM resources and virtual allocation can offer huge potentials to reduce costs over time. You can also use virtual machine resource allotment tools to discover best practices for the future, which you can reference to predict and prepare for future virtual machine resource complications. This will help you cut budgets set aside for troubleshooting and prevent costly last-minute scrambles for VM resources.
Here are a few metrics you can monitor using virtual machine resource allocation software:
- CPU average utilization
- Network average utilization
- Disk I/O
- Disk space utilization (max)
- RAM utilization (max)
There are many virtual machine resource allocation tools available to choose from, and it can be difficult to decide which software is best for you and your VM environment. Below, I’ll go into the details of two great tools designed to monitor and manage VM resources and virtual allocation within your network.
Recommended Tools for Monitoring VM Resources
SolarWinds Virtualization Manager
My top choice for a virtual machine resource allocation monitoring tool, and a tool for managing general VM resources and operations, is SolarWinds Virtualization Manager (VMAN). VMAN is designed to offer comprehensive monitoring capabilities of your VM environment and optimize troubleshooting across virtual machines. Powerful capacity planning tools support new workloads and enable you to make tough decisions on virtual machine resource management and virtual allocation across your IT infrastructure.
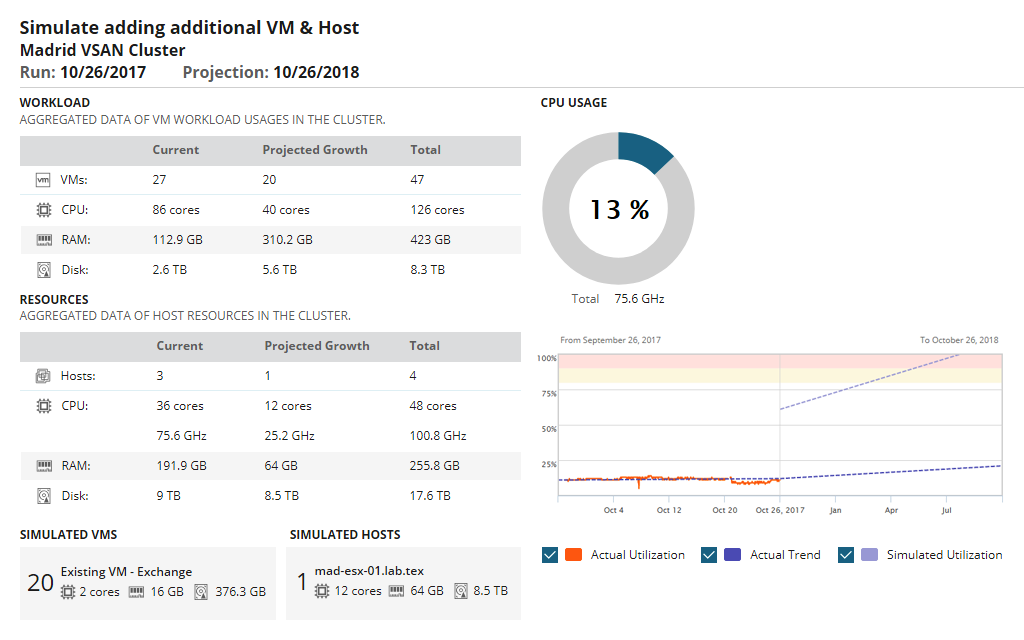
Speed up problem resolution with help from VMAN, which is designed to correlate problematic events to specific virtual machines. This will enable you to pinpoint which specific VM is malfunctioning and why, allowing you to quickly discover root sources of performance issues. VMAN is also designed to monitor VM sprawl by highlighting virtual machines sitting idly and those scrambling for more resources, enabling you to immediately resolve related problems and improve VM resource allocation.
VMAN offers automated discovery tools to help you dive into insights regarding your virtual machine processing and resource allocation. These vital statistics are designed to appear on simple yet powerful dashboards, displaying important virtual machine resource metrics on a single pane. VMAN’s customizable dashboards can show health maps of your VM infrastructure using different views, including the environment view designed to automatically map VMs to their dependent hosts, datastores, and related objects. VMAN dashboards supply quick glances into VM resource and performance issues while giving you the option to examine further details of specific events.
VMAN is designed to track virtual machine configuration changes in Hyper-V and your entire IT environment, enabling you to identify root causes of issues potentially stemming from configuration manipulations. Maintain these changes to prevent amendments from negatively impacting your VM performance, and monitor deviations using baselines automatically generated through VMAN. Understanding the changes in your VM resources and activity will help you easily spot startling fluctuations and prepare for any future challenges.
Along with virtual allocation statistics, VMAN could let you access virtual machine storage metrics of top datastores by IOPS and latency. Doing so will help you avoid bottlenecks, reduce downtime, and recover VM resources by efficiently solving performance issues. You can analyze I/O storage along with latency and failures, which are the most common performance issues in Hyper-V tools, using VMAN’s time travel feature. This feature enables you to view full historical accounts of VM configuration data and relationships, enabling you to identify dependencies from a specific time during Hyper-V virtual processor allocation. You can also use the time travel feature to pinpoint specific virtual machines present in your OS, such as which VM belonged to which host a given time or which VM generated the most I/O operations at a certain moment.
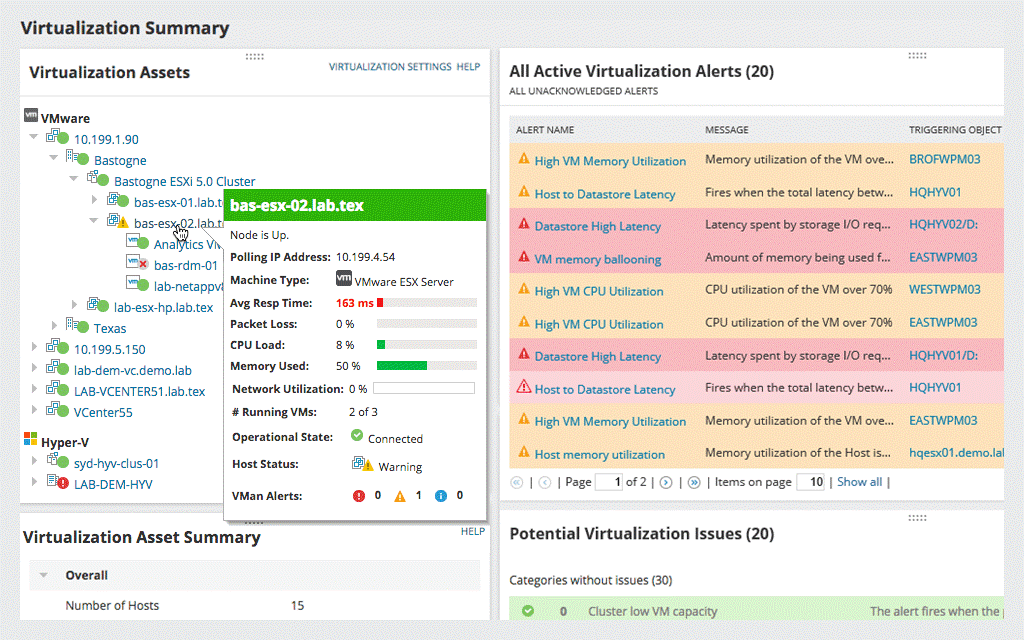
VMAN comes with some other useful features such as the virtual DNA feature, designed to hold historical records over time, so you can compare VM configuration changes throughout history. You can enable alerts to come through VMAN, and these alerts could cover updates on CPU, memory, storage performance, disk bottlenecks and latency, memory ballooning or swapping, and more. VMAN allows you to customize these alerts and their thresholds to adjust for your specific network needs and requirements. VMAN also features SolarWinds AppStack™, which quickly consolidates data gathered throughout your IT vendors to offer you personalized performance recommendations and best practices. I recommend SolarWinds VMAN as the first tool you should try. The cost of this software starts at $1716, and offers a 30-day free trial.
ManageEngine OP
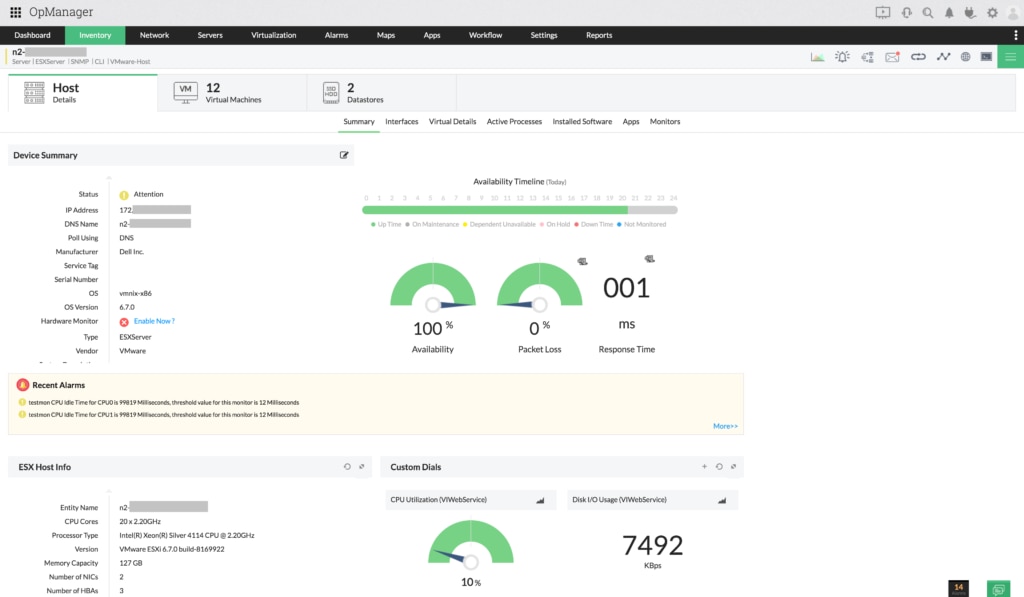
My second suggested tool for managing your virtual machines is ManageEngine OP, designed to generate insights that help resolve problems before users are affected. Like VMAN, ManageEngine OP can offer feedback on virtual machine resource allocation, so you can plan for the future. Also, like VMAN, ManageEngine OP supports physical plus virtual monitoring of your virtual allocation along with other network configuration management tools.
One of these tools, again like VMAN, is ManageEngine OP’s customizable dashboards. These dashboards included widgets, capacity planning tips, and at-a-glance graphs and charts to support file sharing. ManageEngine OP could also provide alerts and send reports to IT administrators, so they can ensure uptime and peak performance. View performance statistics, bandwidth consumption, and more configuration management metrics on a single snapshot page supplied to provide you and your team with valuable insights.
Whereas VMAN is all-encompassing, ManageEngine OP supports scalability and the potential to bring add-ons into your virtual machine resource allocation monitoring infrastructure. The three differing levels of ManageEngine OP—Standard, Professional, and Enterprise—offer unique features and capabilities, although some tools require a special license to function. Enterprise includes hardware and workflow monitoring, device monitoring, alarms and notifications, failover/high availability, and 3D rack plus business views for VM processor monitoring. You can download a 30-day free trial of all three ManageEngine OP levels.
Concluding Thoughts on VM Processor and Resource Allocation
When it comes down to it, SolarWinds VMAN can be a great choice for monitoring your virtual machine resource metrics and VM resources while maintaining optimal virtual allocation and Hyper-V virtual processor allocation. Properly managing your virtual machine resource allocation with VMAN will enable your network to run multiple tasks simultaneously and successfully without compromising speed, disk storage space, or resources, and without causing detrimental performance issues within your VM processors and hosts. I personally use this tool in organizations I work for—both small IT companies with their own server facilities and large organizations often using external virtualization solutions such as virtual machines in the cloud. The VMAN software I recommend has proven itself on every scale. Download a 30-day free trial of VMAN today, so you can start expertly keeping track of your virtual machine resource allocation and optimize VM processor performance.


