You might be asking yourself, what is an audit log and how do I use it? Understanding how a log audit operates and why an admin might want to audit their logs is crucial to business success. In fact, effective audit log management supports compliance, accountability, and security.
Audit log management often goes overlooked in favor of more urgent concerns. However, this guide will explain why putting audit log management on the backburner is a mistake. This guide explains what log audits are, their importance, and how you can make the most of them. I’ll also suggest log auditing software suitable for business use and among the best on the market today.
What Is an Audit Log?
Advantages of an Audit Log
How to Conduct a Log Audit
Best Log Auditing Software
What Is an Audit Log?
An audit log, also called an audit trail, is essentially a record of events and changes. IT devices across your network create logs based on events. Audit logs are records of these event logs, typically regarding a sequence of activities or a specific activity. Audit logs don’t always operate in the same way. In fact, they vary significantly between devices, applications, and operating systems. But typically, they capture events by recording who performed an activity, what activity was performed, and how the system responded.
Audit logs take note of just about every change within a system, providing a complete track record of your system’s operations. Therefore, audit logs are a valuable resource for admins and auditors who want to examine suspicious activity on a network or diagnose and troubleshoot issues. These audit logs can give an administrator invaluable insight into what behavior is normal and what behavior isn’t. A log file event, for example, will show what activity was attempted and whether it succeeded. This can be useful when identifying whether a system component is misconfigured or likely to fail.
Audit trails can either be manual or electronic records, although the term typically refers to digital records. A log audit could be as simple as a basic file or database table, but it needs some structure to avoid becoming confusing. Some people may use an audit log review template, which will give you a tried and tested structure and format. This means you just have to input your logs. If you think an audit log review template might be suitable for you, there are audit log examples accessible online, or they should be embedded within your auditing software.
One trouble with audit logs is they’re vulnerable. If a log audit is misconfigured, corrupted, or compromised in some way, it becomes useless, so understanding the basics of audit logging is very important. The most basic forms of audit log management and event log auditing—like manually combing through your records, device by device—are only suitable for small-scale enterprises. If you want something scalable, robust, and less prone to human error, then log auditing software is a necessity.
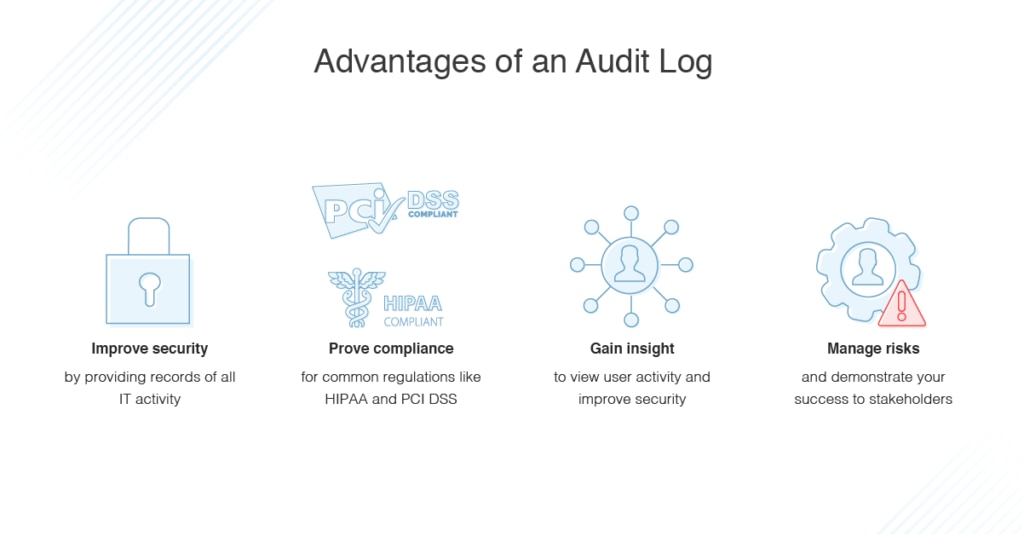
Advantages of an Audit Log
Audit logs offer benefits and advantages for both IT teams and businesses.
Improving Security
Audit logs help with security because they provide records of all IT activity, including suspicious activity. Audit logs can assist with monitoring data and systems for any possible security breaches or vulnerabilities, and with rooting out internal data misuse. Audit logs can even be used to certify document protocols are being complied with and for tracking down fraudulent activity.
Event log auditing is also important for cybersecurity because it provides records that can serve as evidence. A comprehensive and in-depth log audit can make all the difference in the event of a legal battle and can protect your business from liability.
Proving Compliance
Externally, audit logs are critical for proving compliance with common regulations like HIPAA and PCI DSS. Audit logs serve as an official record businesses can use to prove they were in compliance with the law. For many businesses, it’s necessary to share logs with auditors on a regular basis, especially if an issue occurs. Using audit logs to comply with regulations can protect businesses from major fines and penalties.
Gaining Insight
Network engineers, help desk staff, developers, and administrators are likely to use log audits internally to boost performance, increase accountability, and keep the system stable. Log files provide historical visibility into activity, so changes won’t go overlooked.
Audit logs record how often someone accesses a certain document or file, which can give a company invaluable insight. You can use a log audit to learn about user activity, which could be used to boost efficiency, security, and performance.
Risk Management
Having a robust risk management strategy is important for any business. Audit logs play a key part in risk management because they let you show partners, customers, and regulators you’re taking measures to prevent issues before they occur. This could show an investor you pose a reliable and low-risk investment opportunity.
How To Conduct a Log Audit
First and foremost, you should understand what fields to audit when an event occurs. The information included in the log should provide the context of the event, the “who, what, where, and when,” and anything else of relevance. The following fields are critically important:
- Group (i.e., the team, organization, department, or account from which the activity originated)
- Actor (i.e., the uuid, username, or API token name of the account responsible for the action)
- Event name (i.e., the standard name for the specific event)
- Description (i.e., human-readable, may include links to other application pages)
- When (i.e., the server NTP synced timestamp)
- Where (i.e., the country of origin, device identification number, or IP address)
- Action (i.e., how the object has been altered)
- Action Type (i.e., create, read, update, or delete)
You might also include the server ID or name, server location, the version of the code sending the event, the protocols (i.e., https or http), and the global actor ID.
Before deciding what degree of auditing is necessary, you should conduct a risk assessment for each system or application. At the very least, however, you’ll have to log the following: user IDs, date and time of logging in and logging off, failed and successful access attempts, terminal identity, networks accessed, files accessed, system configuration alterations, system utility usage, security-related events, exceptions, network connection changes or failures, attempts to alter security settings, and the activation of protection systems like anti-malware. These components contribute to access control monitoring, allowing you to investigate audit trails if there’s an incident.
Making sure you sync the timestamp is another key element of log audit management. Without the logs timestamp field using a common format, it would be practically impossible to conduct sequential analysis. NTP, time protocol, should be synchronized for all servers, devices, and applications, as this is a compliance requirement for numerous standards.
Log file security is also important. Log audits are prime targets for anyone intent on hiding evidence of their activity or wanting to compromise and corrupt data. To prevent this from happening, it’s best practice to configure audit logs so strong access control restrictions are established for the logs. This usually includes limiting the number of users who can change log files. It is also best practice for all transmissions of audit logs to be encrypted.
Best Log Auditing Software
Log audits are a difficult business. Though they’re important for several reasons, a lot goes into maintaining them, and manually managing your own logs can be both a time-consuming and error-prone process. If you want to free up time and make your log auditing operations more efficient, then SolarWinds® Log Analyzer, SolarWinds Security Event Manager, and SolarWinds Access Rights Manager are the best tools money can buy.
All three of these tools boast user-friendly, dynamic dashboards that display data in a graphical, easy-to-interpret way. Security Event Manager automatically monitors your application security audit logs, detecting issues in real time. Abnormalities are flagged, and the program gives you relevant security recommendations. It analyzes server log data and provides color-coded results, helping you prioritize the most important elements.
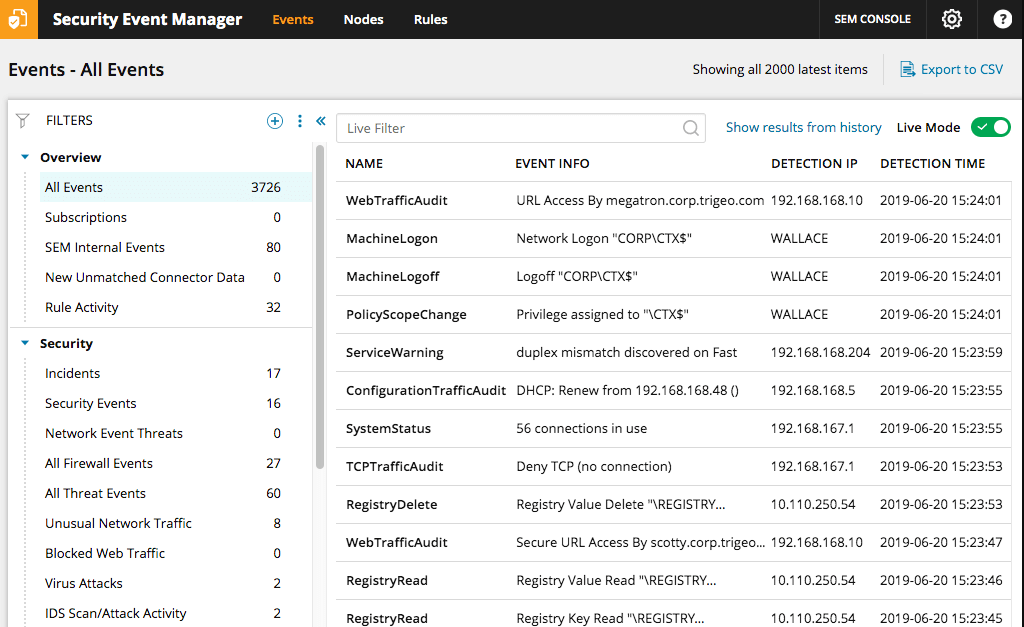
Security Event Manager also helps streamline account control and prevent privilege abuse, alerting you whenever to unusual logins or data modification. The program can decommission any suspicious accounts and lets you reassign security groups quickly and easily. This software is also great for demonstrating compliance, because it lets you generate security reports specifically designed to show compliance with GLBA, SOX, NERC, HIPAA, and more. A free trial of Security Event Manager is available.
Log Analyzer, a log management and analysis program by SolarWinds, takes a more performance-based rather than security-focused approach to log audits. This tool allows you to perform log data analysis on server and network devices. You’re afforded key insight into a range of information types, including SNMP traps, syslogs, and Windows event logs. With all this near real-time critical log data collection, centralizing, and analysis, your troubleshooting can be more accurate and happen more quickly.
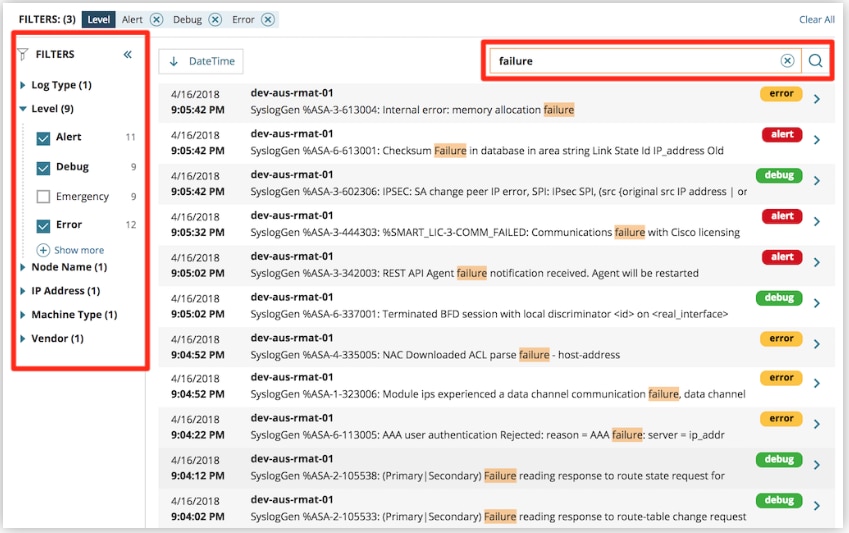
Another benefit of Log Analyzer is it lets you filter your log data via an intuitive, built-in search engine. You can refine your search with out-of-the-box filters like log type, node name, machine type, vendor, and more. Searching your logs couldn’t be easier.
One of the best Log Analyzer features is its data visualization features, including interactive charts. This assists with rapid and accurate analysis, in addition to unifying infrastructure performance. A free trial of Log Analyzer is also available.
If you’re looking for a tool focused on access rights, you need SolarWinds Access Rights Manager. This tool offers ongoing visibility into the access rights of everyone on the network. Compliance requirements demand granular and comprehensive insight into user access rights, and with ARM, you can easily check who has access to critical and sensitive data. What’s more, if suspicious changes or activity take place, ARM instantly sends an alert.
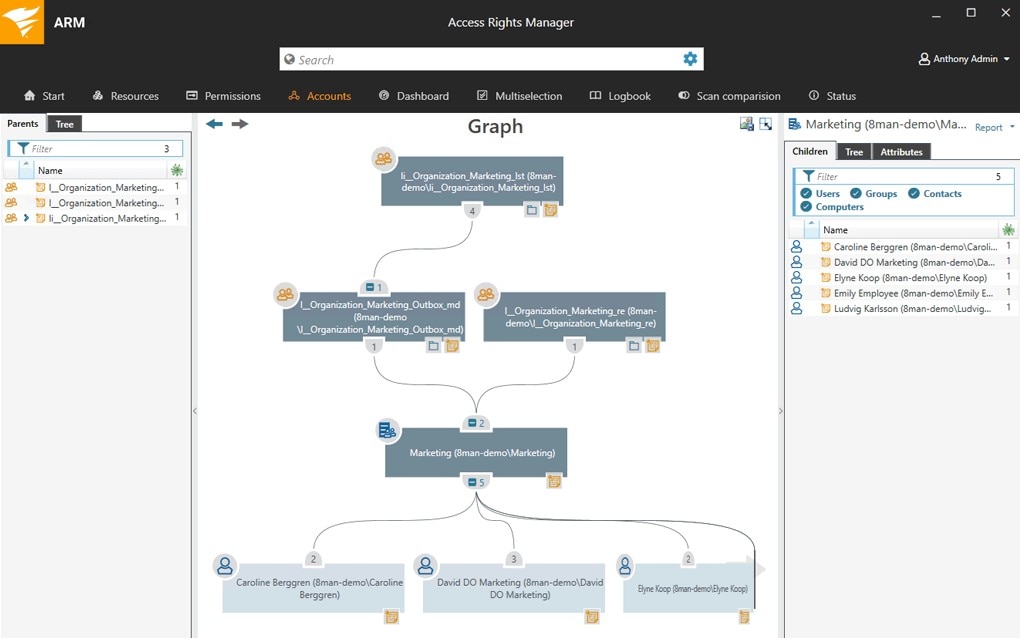
In terms of audit logs, it’s easy to use ARM to generate the custom reports you need—you can use audit reports to track user provisioning and behavior internally, while for auditors, you can prove you’ve handled access rights according to compliance regulations. Try ARM free for 30 days.


