Virtual infrastructure is vital to many business IT environments, with the potential to add significant efficiencies and cost savings if you deploy and use it properly. Physical infrastructure takes up a large amount of space and can be easily replaced with virtual infrastructure if you set it up correctly and follow best practices for managing it. In this guide, we’ll review what virtual infrastructure is and why you might use it, followed by some key tips for virtual infrastructure management and planning.
In enterprise settings, I recommend using professional tools to assist with virtual infrastructure management, as the processes can become complex. My choice is SolarWinds® Virtualization Manager (VMAN), in part because its high-quality and easy-to-use features work well with a wide range of virtualization platforms and hypervisors.
Physical vs. Virtual Infrastructure
Physical infrastructure encompasses things like physical servers, in which software runs on hardware. The hardware includes memory, network cards, and chips, and processing and storage resources. You install an operating system (such as Windows) on the hardware, and run software through the OS.
Virtual infrastructure uses physical infrastructure, but instead of installing an operating system, you install a hypervisor. A hypervisor is a special kind of software that runs virtual machines, or VMs. Hypervisors can either be installed directly onto the hardware (in which case it’s called a “bare-metal hypervisor”) or they can be installed on the operating system (a “hosted hypervisor”). Both kinds of hypervisors create virtual machines, which use the physical hardware.
With virtual machines, you can have more than one running on a single physical device. Instead of needing, for example, 10 physical servers, you can have one physical server with a hypervisor running 10 virtual servers, all using the hardware simultaneously.
Virtual machines can run applications just like physical machines. You can install different operating systems on the virtual machines than you can on the OS on which the hypervisor is installed. For instance, you could have a hosted hypervisor installed on Windows, and then run a virtual machine with Linux installed.
In an enterprise setting, virtual infrastructure can mean you have numerous servers and physical resources in a server room, or in a data center to store the data for your business.
Benefits of Virtual Infrastructures
Virtual machines and virtual infrastructures have many benefits, including:
- Virtual infrastructures make better use of hardware resources because each virtual machine can take and use what it needs, when it needs it. While some machines are active, others will be in downtime or low-use phases. This translates to less resource wastage.
Keep in mind, however, if you need a huge amount of performance power all the time, virtual infrastructure may not be your best option. - With virtual machines, you can run operating systems and install applications that would otherwise not be compatible. This allows for broader development and application testing capabilities.
- Virtual machines are separate from each other, which creates a security barrier between them. This makes them less vulnerable to viruses, bugs, and other problems that can be carried through a network.
- Virtual machines are easily portable, so you can move them between servers without problems.
- Virtual servers scale easily, accommodating rapid organizational changes in needs.
- Virtual infrastructure is much more resilient to disasters and problems, as restoring from previously created VM backups is typically fast and efficient.
Virtual Infrastructure Management
The benefits of virtual infrastructure are clear, but it’s important to manage your virtual infrastructure correctly. VMware vSphere and Microsoft Hyper-V are two common hypervisors. These manage the virtual machines under their control.
One of the key things you need to keep an eye on is your virtual infrastructure capacity. When you’re running multiple workloads simultaneously, and you have a virtual infrastructure setup dependent on a physical infrastructure, realistically determining capacity and predicting trends is critical. Failing to take multiple workloads into account can lead to negative consequences.
In addition, since VMs can be created so easily, you run the risk of a problem at the other end of the scale: virtual machine sprawl. This is where you end up with a quantity of virtual machines beyond what you need, which can become extremely inefficient. This can cause performance problems and resource wastage.
Another thing to watch is the performance of your virtual infrastructure. Problems with performance can, as mentioned above, be caused by capacity issues if you haven’t kept on top of them properly. Performance issues can also be caused by incorrectly configured virtual machines, or a setup where too many virtual machines are using one piece of hardware.
Be sure to have a clear lifecycle management plan in place, to ensure your software and hardware is all healthy and not nearing the end of its life. Control resources and wastage carefully and maintain a running inventory (which I’ll talk about more below).
You also need to keep tabs on security for your virtual infrastructure, in the same way you would protect physical infrastructure. Just because VMs are less vulnerable to attack doesn’t mean they can’t be targeted.
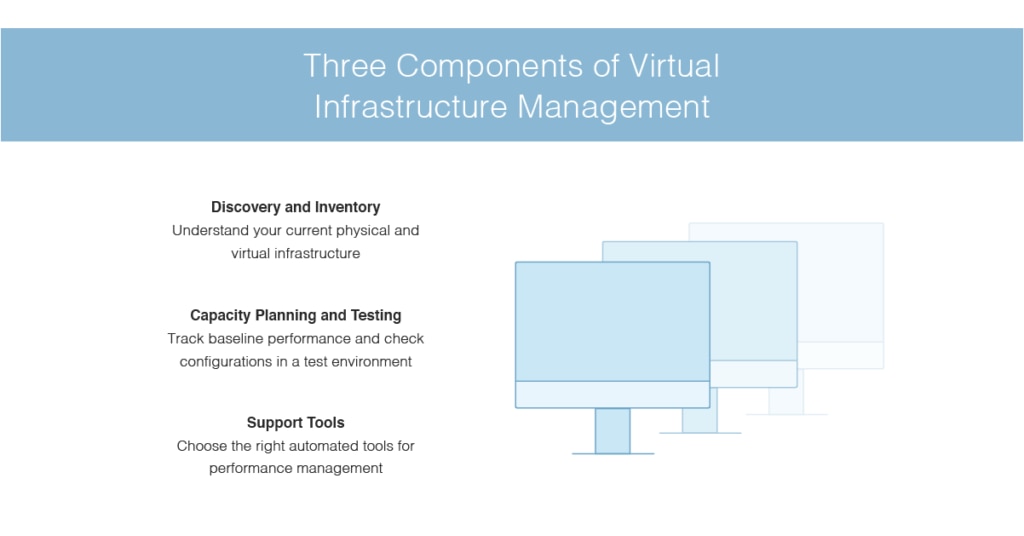
Three Components of Virtual Infrastructure Management
There are three foundational components of effective virtual infrastructure management: discovery and inventory, support tools, and virtual infrastructure capacity planning.
Discovery and Inventory
The starting point is to discover and inventory your entire virtual infrastructure. It’s impossible to conduct proper performance monitoring and troubleshooting if you don’t know what physical and virtual infrastructure you have. You should maintain a running inventory, which means it should be updated and recorded every time something changes.
Support Tools
One of the most important parts of managing virtual infrastructure is the use of automated tools. In addition to taking the pressure off IT staff, who no longer need to manage everything manually, the right tool makes it easy to conduct processes such as running inventory checks. I recommend SolarWinds VMAN. It includes features for performance management, capacity planning, sprawl management, and application management, and predictive recommendations to help you make fast and well-supported decisions.
VMAN includes out-of-the-box virtual server monitoring tools, which are a great help when it comes to general virtual infrastructure management. You can use the VM capacity planning feature to monitor, track, and model and predict CPU, memory, network, and storage needs for your virtual environments, and easily figure out whether you need to increase your hardware purchases.
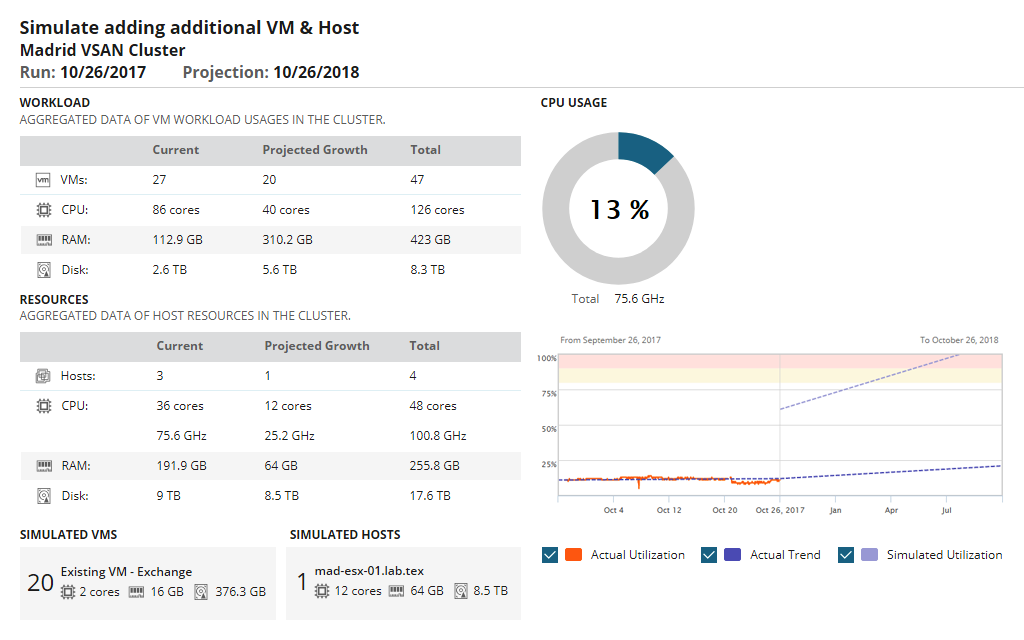
The performance management features in VMAN also allow you to look carefully at virtual server performance correlations. Its interactive and customizable performance dashboards show you how VMs are mapped to their underlying host, storage, and related objects, which helps you quickly trace through performance problems to find the root cause. In addition, you can view storage-related performance metrics, including metrics pertaining to hardware health, historical performance data, and configuration changes.
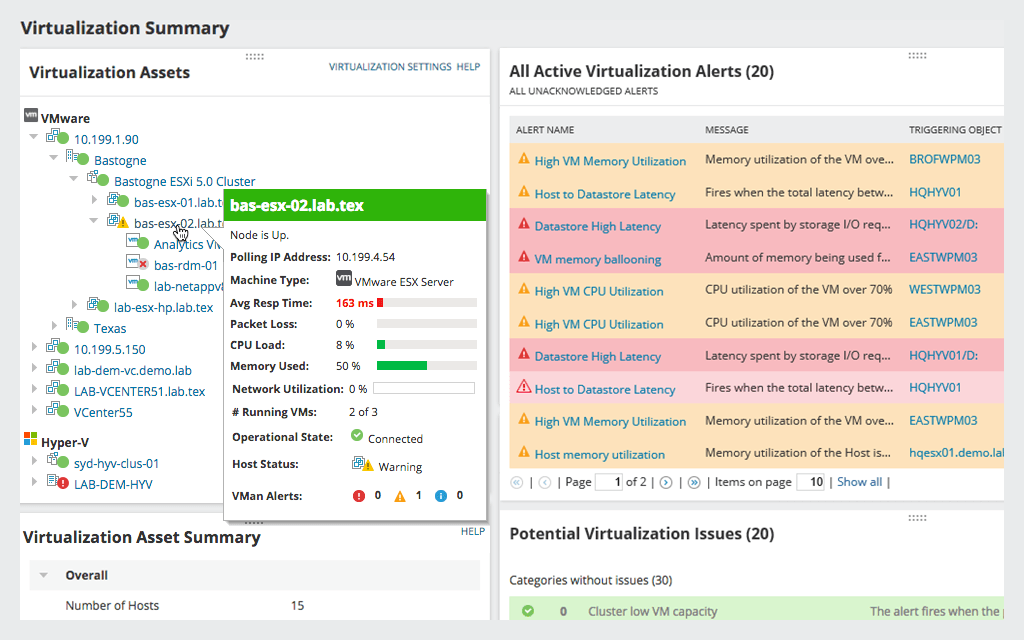
SolarWinds Virtualization Manager can integrate with the scalable SolarWinds Orion® Platform to provide additional functionality. A free trial of VMAN is available through the SolarWinds website, fully functional for up to 30 days. You can also access an interactive demo of this and other SolarWinds offerings.
Capacity Planning and Testing
The third important part of the management process is to engage in thorough capacity planning and testing for your virtual infrastructure. Capacity planning entails looking at the baseline performance and needs of your system to determine where you might experience spikes in need, and where you might need more (or fewer) virtual servers or VMs. You then need to test the performance of your various configurations.
To do this, you’ll first need to build a test environment. You can then run your different scenarios and see how they perform. Once you have your results, you can scale each of your scenarios to match “low,” “average,” and “high” workloads, to look at whether your virtual infrastructure setup still works as expected.
Managing Your Virtual Infrastructure: Key Takeaways
Virtual infrastructure can become a core part of your business, if it hasn’t already, and treating it with appropriate management approaches is vital. Without well-thought-out virtual infrastructure management and capacity planning, you may end up with poorly performing systems, storage, applications, and services.
As part of the management process, you need to be engaging in thorough discovery and inventory to keep track of your virtual infrastructure. It’s also essential to undertake capacity planning and testing. By doing so, you can shore up your system against bottlenecks and other performance problems—and when problems occur, you will be equipped to troubleshoot and find the source.
Finally, use an automated management tool like SolarWinds Virtualization Manager to help you along the way. Beyond helping ensure your processes run smoothly, a good management tool supports performance monitoring, capacity planning, and other important tasks. Trying to do all this manually, or with a collection of standalone tools, only creates more work for you. Choosing an all-in-one professional solution is your best bet for smooth virtual infrastructure management.


